Fig. 1. Repairing disrupted dystrophin.
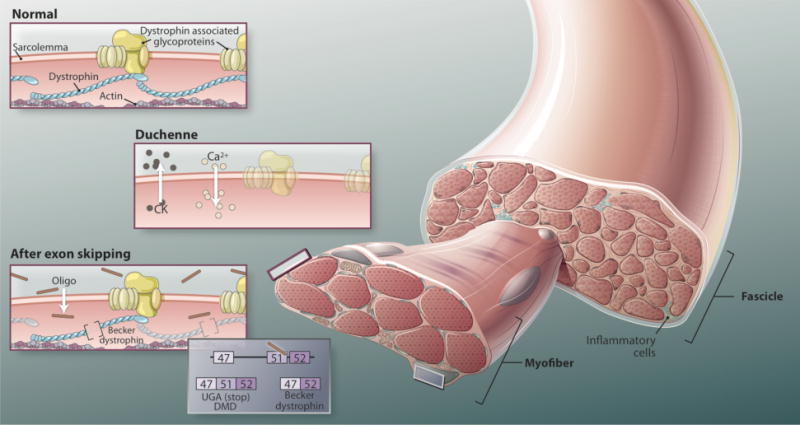
In exon-skipping therapy, for DMD patients are treated systemically with antisense oligonucleotides di- rected against the dystrophin mRNA transcript. These oligos rescue the target mRNA, restoring the proper reading frame and thus protein production. Dystrophin rescue is accomplished by excluding an exon that neighbors a deletion mutation, effectively transforming an out-of-frame (nonsense, loss-of-function) transcript to an in-frame transcript capable of de novo dystrophin production in patient muscle This dystrophin protein lacks some amino acids but retains cytoskeletal function.
