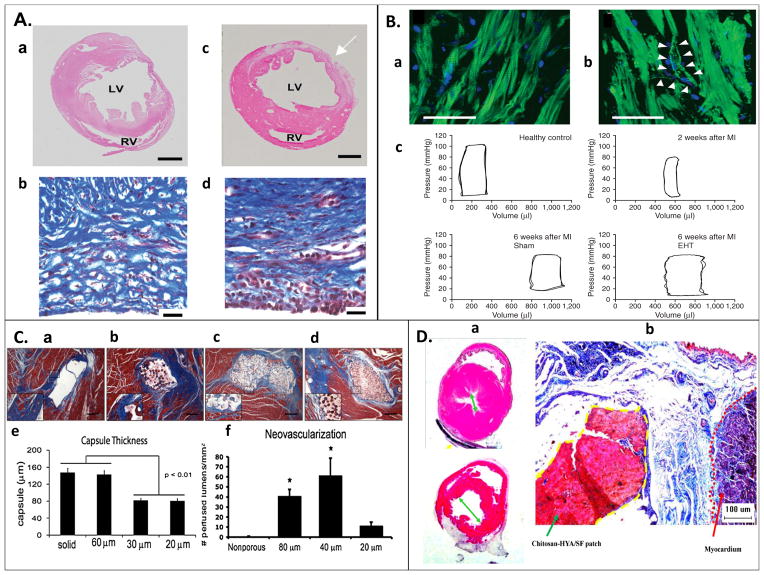
Figure 1. Examples of in vivo studies.
(A) Sections of left ventricle 3 weeks post MI (a) without and (b) with CDC graft, suggesting improved tissue repair with CDC graft. Masson’s Trichome staining of heart wall indicating collagen deposition (blue), and viable muscle cells (red). (d) Specimens with implanted grafts indicated more aligned collagen deposition and higher percentage of surviving muscle cells than (c) non-implanted specimens [43]. (B) (a) Sarcomeric organization in engineered heart tissue (EHT) four weeks post-implantation, stained for actin filaments (green) and nulcei (blue). (b) Putative blood vessel formation observed, with both endothelial and smooth muscle cells. (c) Pressure volume loop of healthy, infarcted, and grafted rat hearts suggest, hearts implanted with an EHT showed less left ventricle dilation and more similar function to normal hearts six weeks post-MI [40]. (C) Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-co-methacrylic acid) hydrogel patch surrounded by collagen capsule (blue) and host myocardium (red) of a nude rat at 28 days after patch implantation. (a) Nonporous and (b) 60μm porous constructs had thicker and denser fibrous capsule than constructs with (c) 30μm and (d) 20μm pores, (e) this thickness was quantified. Neovascularization was more prevalent in the (f) 40μm pore construct, quantified by the presence of rat endothelial cell marker (RECA-1+) on lumen structures [38]. (D) (a) Hematoxylin and eosin stain of heart post MI (b) treated with chitosan-hyaluronan/silk fibronin patch compared to a post MI control presents reduction of left ventricle dilation with the patch treatment. (b) Masson’s Trichome stained heart wall at infarct zone; the dotted yellow line indicates the patch, and the dotted red line indicates the myocardium. The patch adhered strongly to the epicardial surface, and reduced fibrosis in the infarct zone [44].