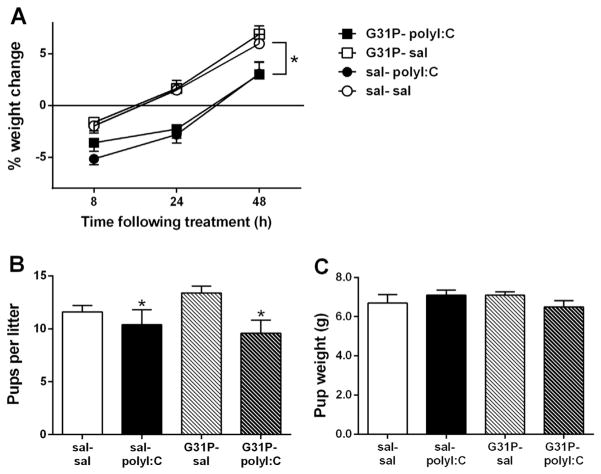
Fig. 2.
Effects of polyI:C and G31P treatment on maternal weight change (A), number of pups per litter (B), and average pup weight at birth (C). PolyI:C treatment caused a significant weight loss in the 48 h following treatment (A) and decreased the number of pups per litter (B), without affecting pup weight (C). Maternal weight change (A) was normalized to the weight of the dams immediately before the initial saline or G31P treatment on gestational day (GD) 15. G31P or saline (500 μg/kg, i.p.) treatments occurred on gestational days 15, 17, and 19. PolyI:C or saline (4 mg/kg, i.v.) treatments were administered on GD15, 60 min after G31P or saline. Group sizes were sal–sal (n = 15 dams), sal–polyI:C (n = 11 dams), G31P–sal (n = 11 dams), G31P–polyI:C (n = 12 dams). B, C. Number of litters assessed for pups per litter and average pup weight was: sal–sal (n = 15 litters), sal–polyI:C (n = 11 litters), G31P–sal (n = 11 litters), and G31P–polyI:C (n = 12 litters). * in panels A and B denote a significant main effect of polyI:C treatment. No significant effects of G31P were observed.