Fig. 1.
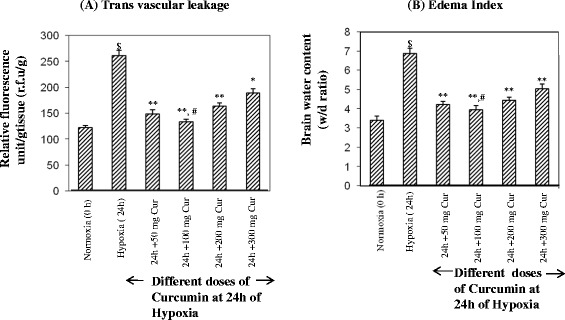
Optimization of curcumin dose in hypoxia-exposed rats. a Transvascular leakage and (b) the brain water content. The rats were pre-treated with curcumin at 50, 100, 200 and 300 mg/kg BW orally 1 h prior to hypoxia exposure at 7620 m for 24 h. The optimum dose of curcumin was found to be 100 mg/kg BW where there was minimum transvascular leakage, and the brain water content and was found to be significantly (p < 0.05) different from other doses of curcumin. Values are mean ± SD (n = 6). $ p < 0.001 compared to normoxia; **p < 0.001 compared to 24-h hypoxia; *p < 0.01 compared to 24-h hypoxia; # p < 0.05 compared to other groups. N normoxia, H hypoxia, Cur curcumin
