Fig. 10.
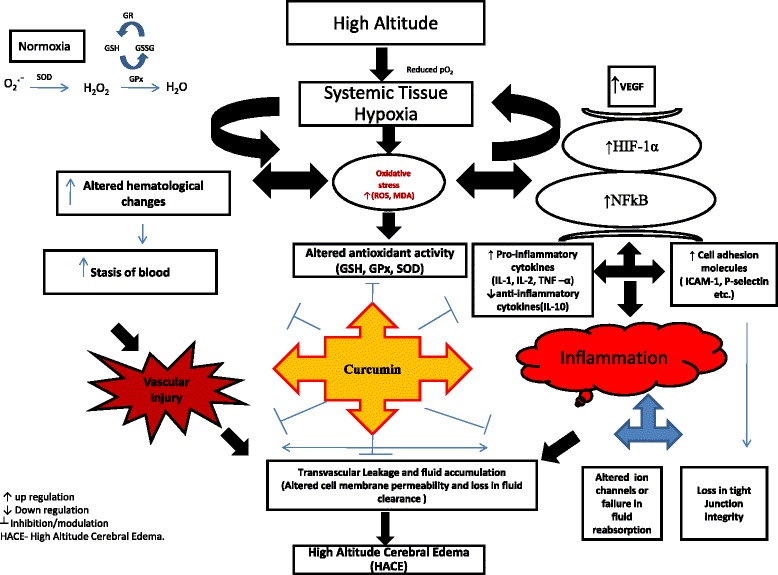
Schematic representation of possible mechanism of action of curcumin against HACE as prophylactic drug. Exposure to hypobaric hypoxia increased the transvascular leakage leading to fluid build-up in the brain due to upregulated NF-κB and HIF-1α and their downstream genes that play a major role in causing inflammation (pro-inflammatory cytokines and cell adhesion molecules) and vascular leakage (VEGF). Further, hypobaric hypoxia exposure impaired the Na+/K+-ATPase and ENaC expression followed by altered tight junction protein (ZO-1, JAMC, claudin 4 and claudin 5) integrity in the brain of rats; whereas prophylactic treatment of rats with curcumin reversed the changes brought by hypobaric hypoxic treatment. Inverted letter T inhibition, upwards arrow upregulation, downwards arrow downregulation, HACE high-altitude cerebral edema
