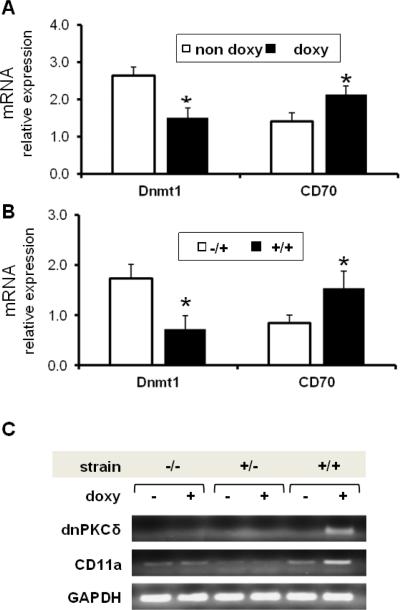
Fig. 4.
Decreased DNMT1 expression correlates with higher CD70 and CD11a mRNA levels in dnPKCδ transgenic T cells. A. Double transgenic animals were given doxy (doxy, n=8) or sucrose alone (no doxy, n=7) in the drinking water for two weeks. CD3+ T cells were then isolated from spleens and Dnmt1 and CD70 mRNA levels were measured relative to β-actin by RT-PCR. *p≤0.03 vs no doxy. Results represent mean ± SE of 4 independent experiments. B. CD3+ splenic T cells were isolated from four CD2rtTA single transgenic animals (−/+) or from five dnPKCδ/ CD2rtTA double transgenic animals (+/+) treated in vitro with doxy for 72 h. Dnmt1 and CD70 mRNA levels were then measured relative to β-actin by RT-PCR as in A. *p≤0.05 vs −/+. C. CD3+T cells isolated from wild type (−/−), single transgenic (+/−) or double transgenic (+/+) mice treated with doxy for two weeks were compared to non-treated animals. mRNA was purified and the expression of dnPKCδ and CD11a were analyzed by PCR amplification using specific primers. The PCR products were resolved by electrophoresis on 0.8% agarose gel. β actin was used as housekeeping gene. Data represent four independent experiments.