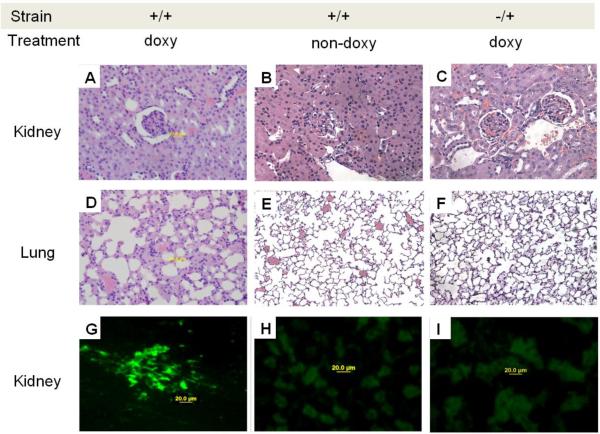
Fig.7.
Glomerulonephritis, pneumonitis and IgG deposition in mice lacking T cell PKCδ activity. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of sections of kidneys from A. dnPKCδ/CD2rtTA double transgenic mice (+/+) treated or B. no treated with doxy or; C. CD2+rtTA single transgenic mice (−/+) treated with doxy for 6 months. A glomerulonephritis with leukocyte infiltration is seen in A. Second row: D. ungs from the same doxy treated double transgenic animals show pneumonitis with leukocyte infiltration as well E. Absence of cell infiltration in animals non-doxy treated or, F. in single transgenic mice treated with doxy. Data are representative of 5 to 7 different animals. Magnification: 400X. G. Representative immunohistochemical staining of kidneys from six dnPKCδ/rtTA double transgenic mice receiving doxy. Intense IgG deposition in all the glomeruli along capillary walls and in the mesangial region is seen. H. Similar staining of representative kidney sections from double transgenic animals receiving only sucrose (n=5) and, I. from single CD2 rtTA transgenic animals receiving doxy (n=5) were used as controls. In both controls, the blank areas are glomeruli with no immune complex deposition. Magnification: 400X.