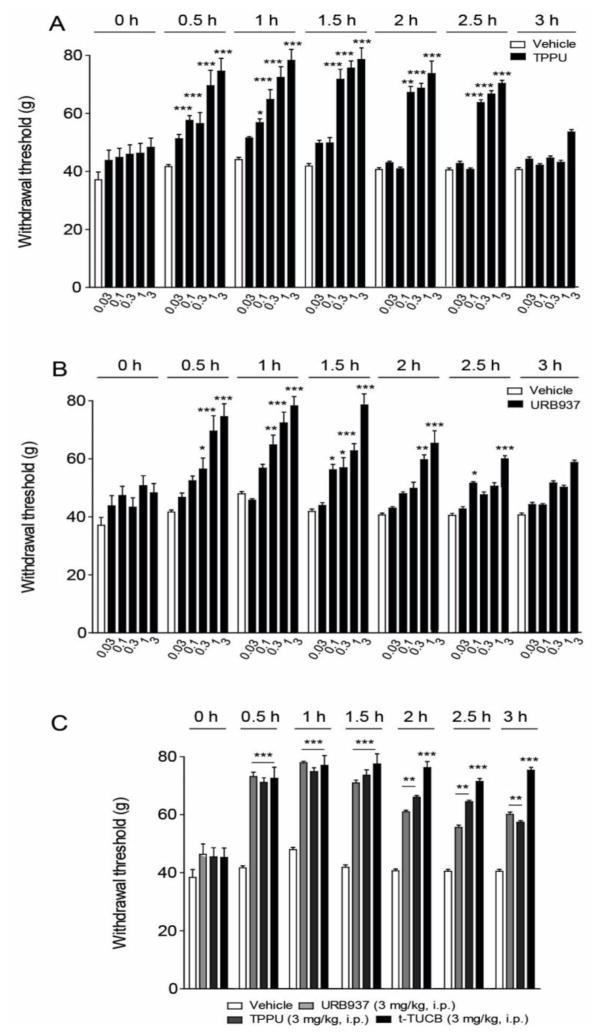
Figure 3.
TPPU and URB937 in single administration reduce diabetic neuropathic pain in rat. (A) The TPPU dose dependent reduction of allodynia was highly significant in diabetic neuropathic rats (P ≤0.001 0.1–3 mg kg−1). (B) URB937 also significantly improved mechanical withdrawal thresholds in neuropathic rats (P ≤0.05 0.1 mg kg−1, P ≤0.001 0.3–3 mg kg−1). The average naïve baseline for groups that were induced for the diabetic model was 78.6±0.9 SEM grams of force to elicit a withdrawal. This value declined with the diabetic neuropathy to a diabetic baseline of 45.2±0.7 SEM. The withdrawal data were compared using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s test for multiple comparisons. (C) The 3 mg-kg−1 doses of TPPU and URB937 are compared with the sEH inhibitor t-TUCB. The sEH inhibition showed similar efficacy at the same dose with two structurally diverse small molecule inhibitors in the chronic pain model. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM (n=6, each group). The data were compared using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s test for multiple comparisons. * P<0.05, ** P< 0.01 and *** P<0.001 vs. vehicle.