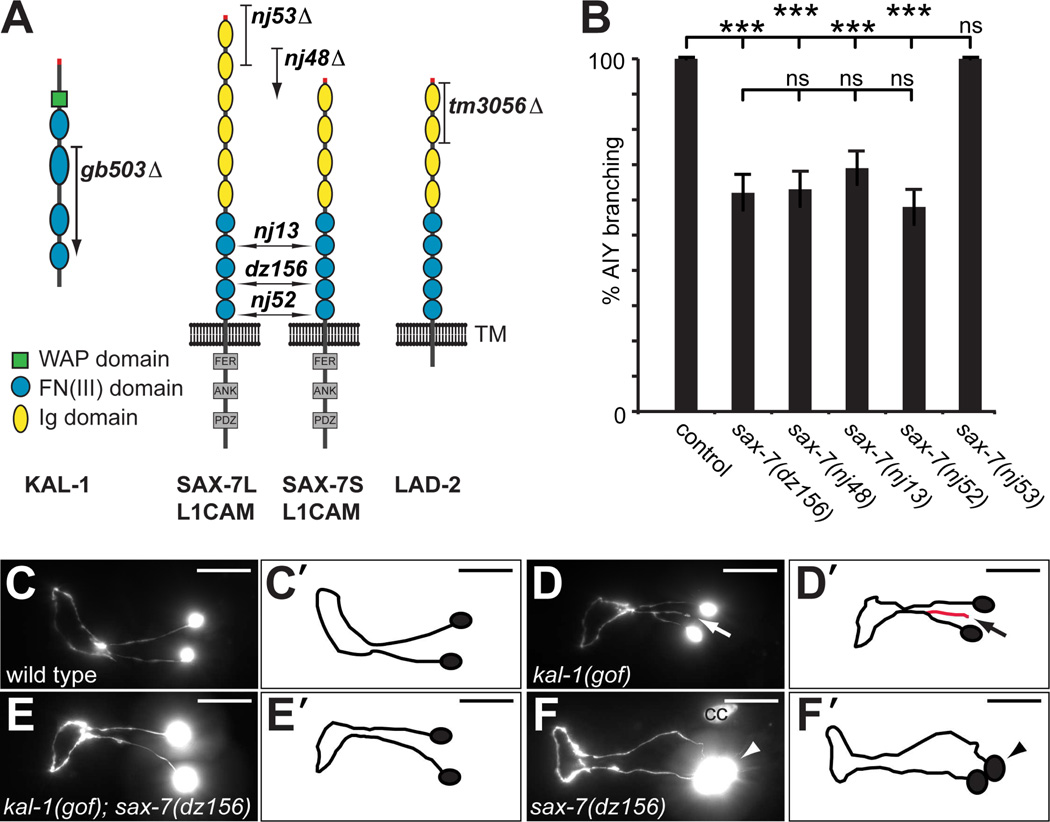
Fig. 1. SAX-7/L1CAM is required for kal-1-dependent axon branching.
A Schematic of the SAX-7/L1CAM and LAD-2 cell adhesion molecules with alleles indicated: nj53 removes the long isoform SAX-7L; nj48, nj13, nj52 and dz156 are deletions, insertions or nonsense mutations and result in premature termination of both SAX-7L and SAX-7S. The tm3056 deletion allele results in a frameshift and removes all LAD-2 isoforms (Wang et al., 2008). Ig: immunoglobulin domain, FN: fibronectin domain III, FER: conserved FERM domain, ANK: ankyrin binding domain, PDZ: PDZ domain.
B Quantification of animals with kal-1/anosmin-1-dependent branches in AIY neurons (% AIY branching) of the genotypes indicated. Generally, AIY interneurons were visualized with mgIs18 (Is[Pttx-3::GFP]) and kal-1 expressed in AIY from the transgenes otIs35X (Is[Pttx-3::kal-1; rol-6(d)]) or otIs76IV (Is[Pttx-3::kal-1; Pcc::GFP]). Statistical significance is indicated: ns: not significant, **: P < 0.005, ***: P < 0.0005. See Dataset S1 for full primary data.
C – F Ventral/sublateral views of adult animals showing the pair of AIY interneurons. Overexpression of kal-1 specifically in AIY neurons results in a branching gain of function phenotype (kal-1(gof), arrow, D,D’) that is not seen in wild type animals (C,C’)(Bülow et al., 2002). This kal-1-dependent branching is suppressed by loss of sax-7 function (E,E’). Loss of sax-7 also results in a cell body positioning defect (arrowhead, F,F’). The nj48 allele of sax-7/L1CAM failed to complement dz156 with regard to the cell body positioning phenotype (Fig. S1A). In all panels, anterior is to the left and scale bars indicate 20µm. cc: coelomocyte.