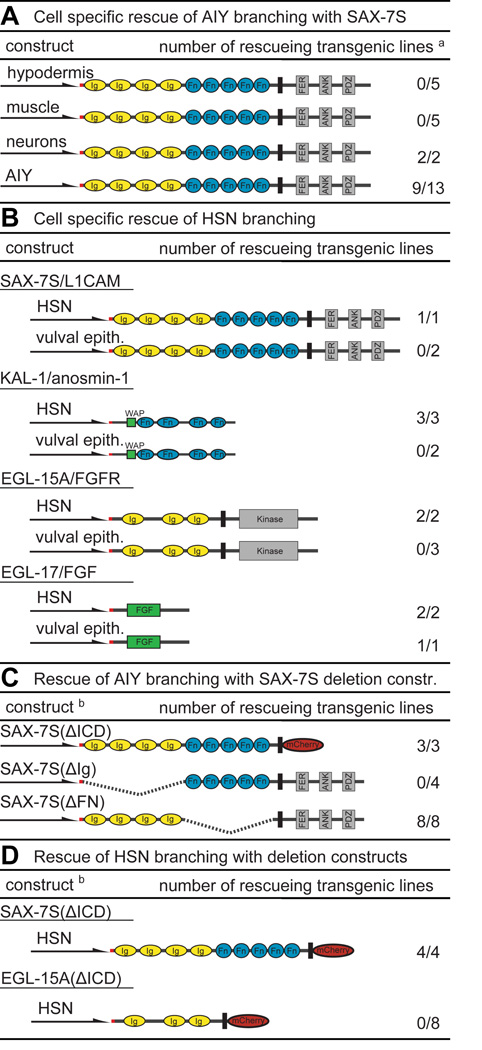
Fig. 3. Summary of heterologous transgenic rescue experiments.
A Cell specific rescue of kal-1/anosmin-1-dependent branching in AIY neurons of sax-7/L1CAM mutants. Schematically shown are the constructs, promoters used (Pdpy-7/hypodermal, Pmyo-3/muscle, Punc-14/pan-neuronal, Pttx-3/AIY) and the number of rescuing out of the total number of lines. Color coding and abbreviation as in Fig. 1. a Rescue in all panels was defined as restoration of branches in transgenic animals and had to be statistically significant (P<0.05) when compared to nontransgenic siblings. N = 100 in all assays. See Dataset S2 for full primary rescue data of all panels.
B Cell specific rescue of branching in HSN motoneurons. An HSN specific promoter (Punc-86)(Shen and Bargmann, 2003) and a promoter that is expressed in the vulval epithelium (Pegl-17)(Burdine et al., 1998) were used to drive expression in the respective tissues. Both promoters have previously been used to determine cell-autonomy of function for genes involved in HSN development (Shen and Bargmann, 2003; Shen et al., 2004).
C Structure/function analyses of SAX-7S/L1CAM in kal-1/anosmin-1-dependent branching in AIY neurons using the Punc-14 pan-neuronal promoter. b In panels (C) and (D), deletions are indicated as dashed lines or by replacement of domains with mCherry: SAX-7S(ΔICD), SAX-7S(ΔIg), SAX-7S(ΔFn) and, EGL-15(ΔICD) which delete the intracellular domains (ΔICD), Ig domains (ΔIg) or FN(III) domains (ΔFN).
D Structure/function analyses of SAX-7S/L1CAM and EGL-15A/FGFR in HSN motoneurons using the Punc-86 HSN specific promoter.