Figure 3. Effects of dexmedetomidine on tau kinases in the mouse hippocampus under normothermic conditions.
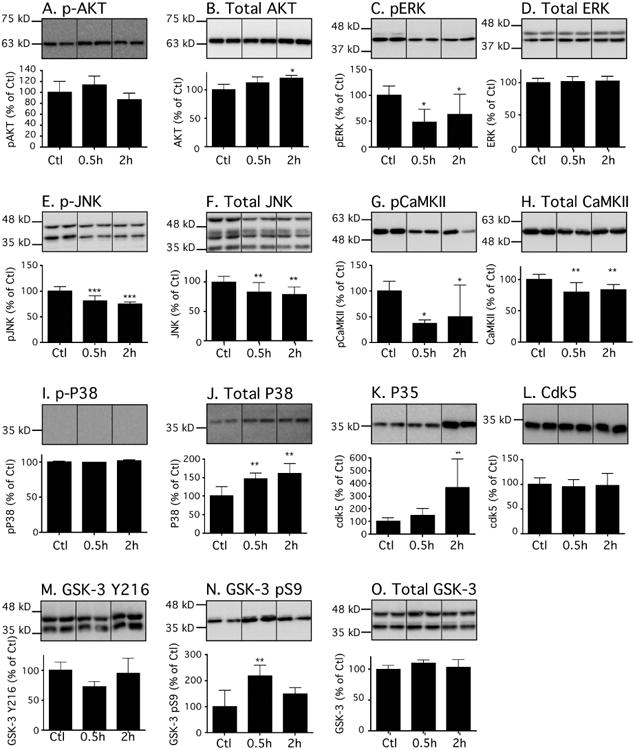
Hippocampal proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, and levels of tau kinases were determined using antibodies directed at activated or total kinases: (A) phospho-Akt, (B) Akt, (C) phospho-ERK, (D) ERK, (E) phospho-JNK, (F) JNK, (G) phospho-CaMKII, (H) CaMKII, (I) phospho-p38, (J) p38, (K) p35, (L) cdk5, (M) phospho-GSK3β pY216, (N) phospho-GSK3β pS9, and (O) (M) GSK3β. Dividing lines represent areas where lanes from the same blot were removed and the remaining lanes were spliced together. Relative immunoreactive band intensities are expressed as a percent of saline control (Ctl) and are displayed for each epitope. For each condition, 1 representative band is displayed with Ctl (n = 6), 0.5h (n = 6), and 2h (n=6). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. *, ** and *** denote P < 0.05, P < 0.01 and P < 0.001 vs. Ctl, respectively; ANOVA with Newman-Keuls post hoc test.
