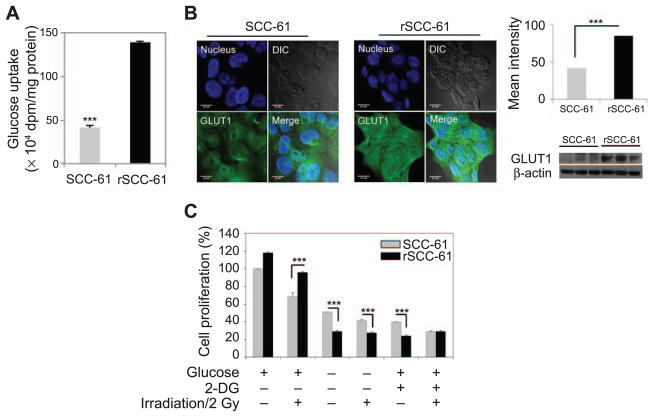
FIG. 1.
Glucose uptake and dependence of cell growth on glucose metabolism in SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells. Panel A: Assay showing increased glucose uptake in rSCC-61 compared to SCC-61 cells (***P < 0.001). Panel B: Imaging analysis of GLUT1 (green) in SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells, quantification of imaging data and validation by Western blot. Blue: Hoechst nucleus staining. The differential contrast images (DIC) and merge panels are also shown. Increased GLUT1 staining and expression by Western blot was observed in rSCC-61 consistent with the glucose uptake data. The scale bars represent a distance of 20 μm (***P < 0.001). Panel C: Glucose deprivation (–) or 2-DG treatment (+) effects on cell proliferation with or without irradiation (–/+). Cell proliferation is expressed as percentage relative to the untreated SCC-61 cells in the absence of radiation exposure. Compared to SCC-61, the rSCC-61 cells have increased requirement of glucose for survival and enhanced sensitivity to the metabolic inhibitor 2-DG regardless of radiation treatment. The statistical analysis is based on three biological replicates (***P < 0.001).