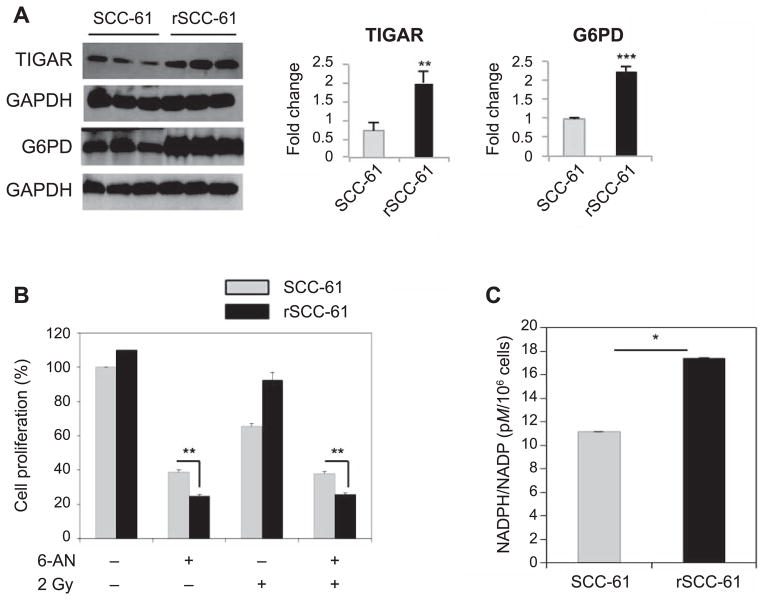
FIG. 2.
Contribution of PPP to cellular proliferation in SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells. Panel A: Western blot analysis showing increased expression of TIGAR (**P = 0.004) and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) (***P < 0.001) in rSCC-61 compared with SCC-61. Panel B: Cell proliferation with or without 6-AN treatment, a PPP inhibitor targeting 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (**P = 0.008) and 2 Gy irradiation (**P = 0.005). Cell proliferation was measured using the sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay and expressed as percentage relative to the untreated control. Three biological replicates were used in this analysis. The results show increased dependence on PPP in rSCC-61 cells compared with SCC-61 cells before and after irradiation. Panel C: NADPH/NADP+ quantification showing increased NADPH in rSCC-61 cells compared to SCC-61 cells (**P= 0.04).