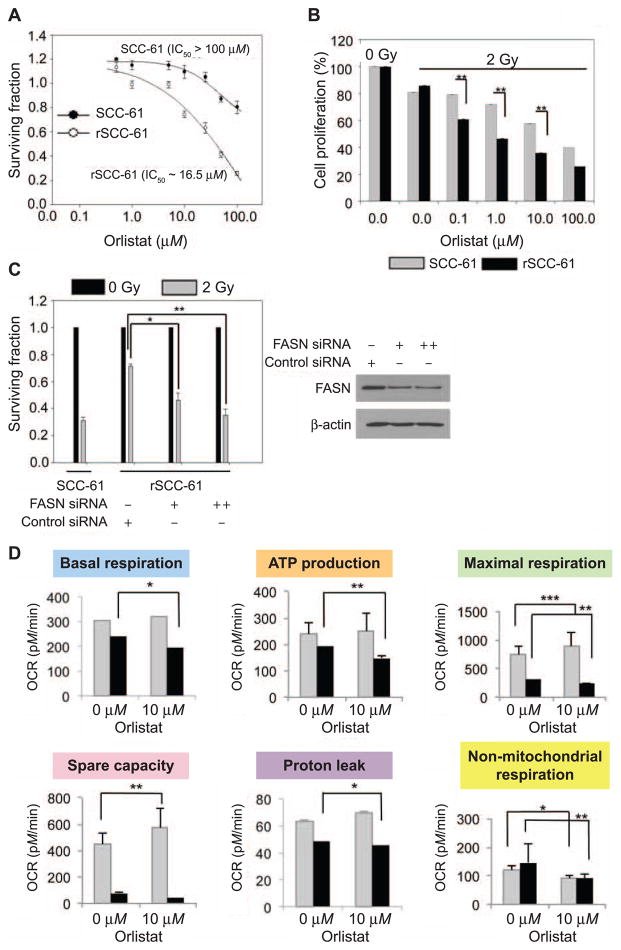
FIG. 6.
Panel A: Clonogenic assay to determine the response to orlistat treatment. The survival plots for the SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells are shown in response to increasing doses of orlistat. The calculated IC50 for orlistat in each cell line is indicated and show enhanced sensitivity to orlistat treatment in rSCC-61. Panel B: Cell proliferation in the presence of increasing concentrations of orlistat and 2 Gy irradiation was determined using the SRB assay (**P = 0.009, **P = 0.005, **P = 0.007 for 0.1, 1 and 10.0 μM orlistat, respectively). Three biological replicates were used for each study. The results show increased sensitivity to radiation after treatment with orlistat in rSCC-61 compared with SCC-61 cells. Panel C: Clonogenic assay to determine the radiosensitizing effect of FASN depletion. rSCC-61 cells transfected with control or FASN siRNA were set up for clonogenic assays and their survival was calculated with 2 Gy irradiation or without irradiation. siRNA-mediated depletion of FASN protein significantly radiosensitized rSCC-61 cells (**P = 0.001–0.01). SCC-61 cells were also set up alongside for the assay for a comparative overview of radiosensitivity. Panel D: OCR for SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells using Seahorse XFA 24-3 after treatment with 10 μM orlistat. Inhibition of FASN by orlistat significantly decreased mitochondrial OCR in rSCC-61 cells and impacted the nonmitochondrial OCR in both SCC-61 and rSCC-61 cells (*P = 0.01–0.05, **P = 0.001–0.01 and ***P < 0.001).