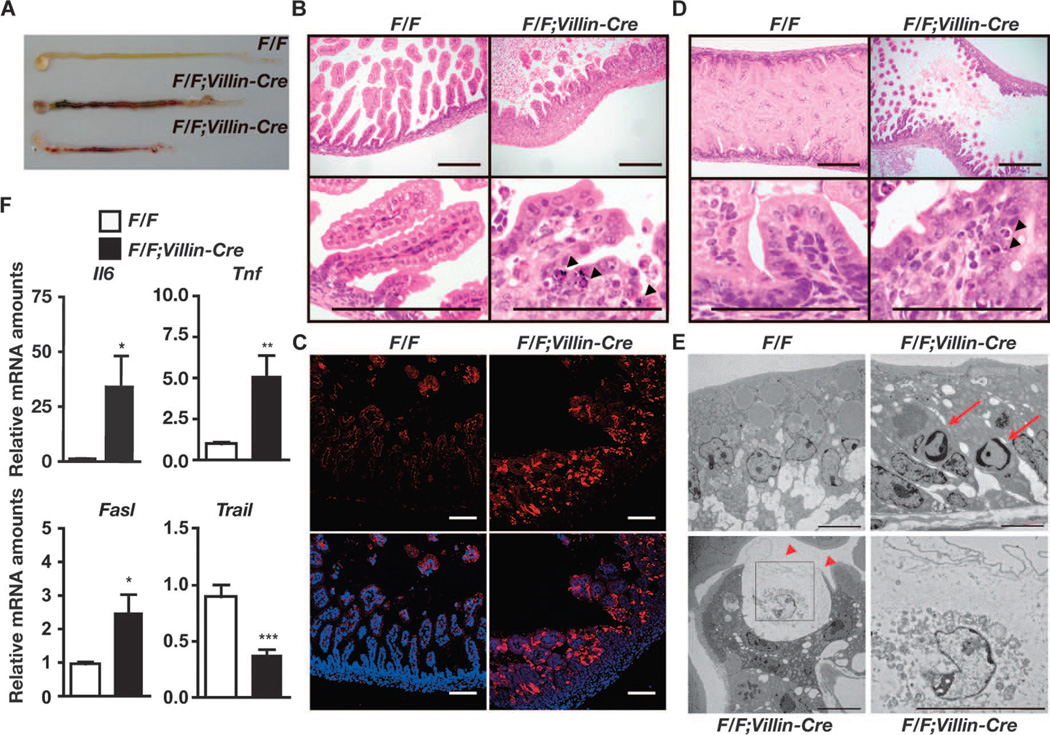
Fig. 1.
Deletion of c-Flip in IECs in mice results in perinatal lethality. (A) Macroscopy of the intestines of c-FlipF/F and c-FlipF/F;Villin-Cre mice. Data are representative of four mice of each genotype. The lower two intestines are from c-FlipF/F;Villin-Cre mice. (B) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained duodenal sections. Arrowheads indicate pyknotic nuclei. Scale bars, 100 µm. Images are representative of four mice of each genotype. (C) Frozen duodenal sections from the indicated mice were stained with anti–active caspase-3 antibody (red) and nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). Lower panels show merged images. Scale bars, 100 mm. Data are representative of four mice of each genotype. (D) Apoptosis of IECs was detected in c-FlipF/F;Villin-Cre mice in utero. H&E-stained intestinal sections of the indicated mice at E18.5 are shown. Arrowheads indicate pyknotic nuclei. Scale bars, 100 mm. Images are representative of two mice of each genotype. (E) Duodenums of the indicated mice were analyzed by TEM. Red arrows and arrowheads indicate apoptotic cells and necrotic cells, respectively. An enlarged image of the black box in the left lower panel is shown in the right lower panel. Scale bars, 2 mm. Images are representative of two mice of each genotype. (F) The amounts of Il6, Tnf, and Fasl mRNAs are increased in the intestines of c-FlipF/F;Villin-Cre mice compared to those of c-FlipF/F mice. RNAs were prepared and their relative amounts were quantified by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Results are means ± SEM of nine mice of each genotype. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared to control mice. Analysis was performed with mice at P0 except for those shown in (D).