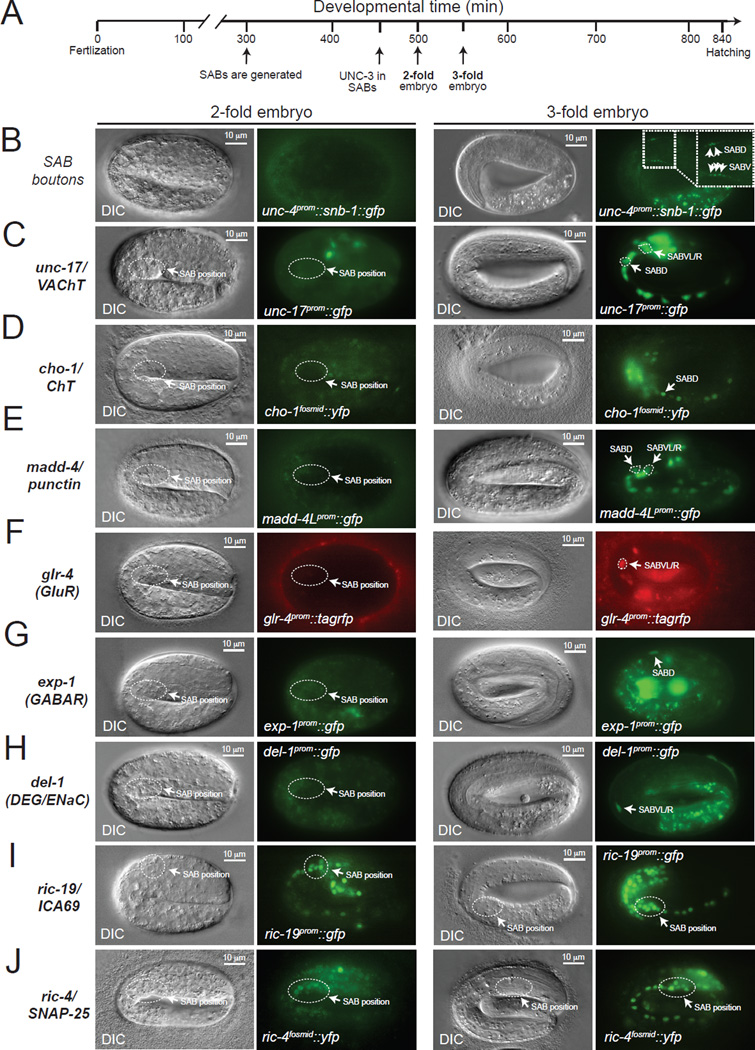
Figure 5. Formation of SAB synapses coincides with the onset of acetylcholine pathway-, synaptogenic-, neurotransmitter receptor- and ion channel-encoding gene expression.
A: Schematic showing key events (SAB generation, onset of UNC-3 expression in SABs, 2-fold embryo, 3-fold embryo) relevant to this paper during C.elegans embryonic development. Developmental time is shown in minutes (min).
B: First synaptic boutons between the SAB MNs and head muscle (as visualized with SNB-1::GFP driven by the unc-4 gene promoter) are observed at 3-fold embryos. SABD and SABV synaptic boutons are shown with arrows (inset).
C–H: The onset of expression of unc-17/VAChT, cho-1/ChT, madd-4/Punctin, glr-4 (GluR), exp-1 (GABAR), and del-1 (DEG/ENaC) occurs at late 3-fold stage embryos. Transgenic animals carrying transcriptional reporters for unc-17 (vsIs48), cho-1 (otIs321), madd-4 (sEx14990), del-1 (wdIs3), exp-1 (wyIs75), and glr-4 (otIs476) were analyzed. These transcriptional reporters are likely to faithfully monitor the endogenous expression pattern of these genes as they contain large cis-regulatory fragments (See Table S6 for details on these reporter strains). To unambiguously distinguish the SAB MNs from other neurons in panels C, D and E, an unc-4prom::mCherry transgene was used as an SAB marker. Arrows indicate cell body position for SAB neurons.
I–J: Expression of synaptic genes shared by all neurons (ric-4 and ric-19) is detected at 2-fold stage embryos using ric-4/SNAP-25 (otIs350) and ric-19/ICA69 (otIs381) reporter strains. See Table S6 for details on these reporter strains.
On the left of each fluorescence image, a differential interference contrast (DIC) image of the worm embryo is shown. The relative position of the SAB cell bodies is shown (dotted circle) in 2-fold and 3-fold embryo panels. Scale bar, 10 µm.