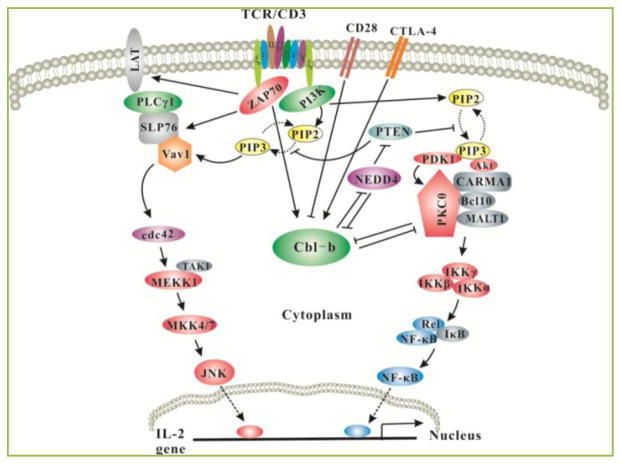
Figure 1. Model of Cbl-b in T-cell activation and tolerance.
Upon TCR stimulation, Pten is inactivated via Nedd4 which targets Pten for K63-linked polyubiquitination, and this process is inhibited by Cbl-b. Inactivation of Pten leads to the accumulation of PIP3 which recruits PDK-1, Vav-1 and Akt to the plasma membrane via its interaction with the PH domains within these molecules. Therefore, Vav1 links PKC-θ to PDK-1, the former coupling IKKs to the CBM complex. Activated Akt also facilitates the formation of the CBM complex possibly by phosphorylating CARMA1. Thus, Cbl-b inhibits NF-κB activation via PKC-and Akt. One of the important outcomes for Akt activation is that Akt-2 can phosphorylate Foxo1/3a which excludes them from the nucleus, thus inhibiting Foxp3 expression (not shown). In anergic T cells, Cbl-b targets PLC-γ1 and PKC-θ for ubiquitination, thus inhibiting T cell anergy induction. The expression of Cbl-b in T cells is controlled by CD28 and CTLA-4. CD28 costimulation induces Cbl-b ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, while CTLA-4-B7 interaction induces Cbl-b expression.