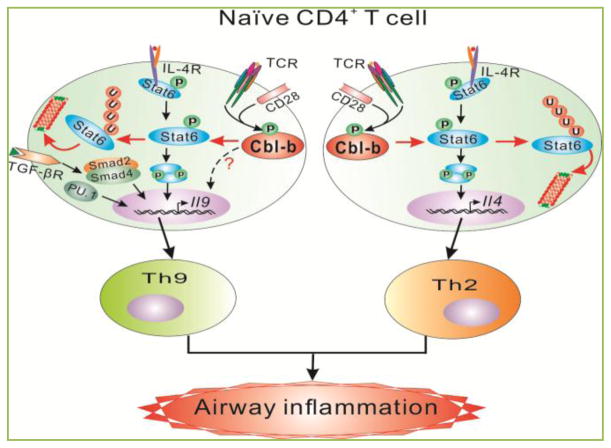
Figure 2. Model of Cbl-b in proallergic T cell development and allergic asthma.
Upon stimulation with TCR/CD28 and IL-4, Cbl-b binds to Stat6 via its tyrosine residues and TKB domain with SH2 domain and phospho-tyrosine of Stat6, respectively. These interactions allow Cbl-b to induce Stat6 polyubiquitination at K108 and K398, which leads to the proteasome-mediated degradation. In the absence of Cbl-b, Stat6 ubuiquitination and degradation is impaired, which results in heightened Th2 and Th9 responses and allergic airway inflammation. Introducing Stat6 deficiency into Cblb−/− mice abrogates hyper-Th2 responses but only partially attenuates Th9 responses, suggesting that Cbl-b regulates Th2 cell differentiation via a Stat6-dependent mechanism but regulates Th9 cell differentiation via both Stat6-dependent and -independent mechanisms.