Fig. 4.
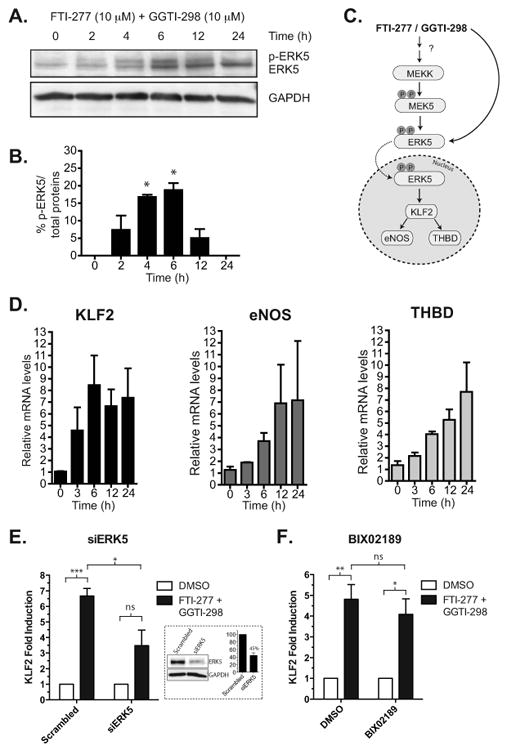
Activation of ERK5 and its downstream targets in the presence of both FTI-277 and GGTI-298 in HUVEC. A. FTI-277 and GGTI-298 (at 10 μM each) in combination increases the levels of p-ERK5 and maximizes at 4 hrs as detected by the pan-ERK5 antibody. B. The level of ERK5 phosphorylation was quantitated by dividing the p-ERK5 band over total protein (p-ERK5 band + ERK5) and expressed as the percentage of total ERK5 protein. The summary bar diagram shows the mean ± SEM of densitometric quantitation from 3 independent experiments. * P value < 0.05, t-test. C. Diagram of the ERK5 signaling pathway. FTI-277 and GGTI-298 could activate the MEKK upstream of MEK5 or directly activate MEK5. Alternatively drug combination could result in alternative direct ERK phosphorylation independent from canonical MAPK signaling (see Discussion). Once activated, ERK5 transcriptionally upregulates eNOS, KLF2, and THBD. D. FTI-277 and GGTI-298 together induced the transcriptional upregulation of known ERK5 targets, including KLF2, eNOS, and THBD, in a time dependent manner. E. siRNA knock down of ERK5 reduces FTI-2777 and GGTI-298 dual drug-induction of KLF2. Cells were transfected with 10 nM scramble or ERK5 siRNA and after 48 hrs treated with drugs or DMSO for an additional 6 hrs. KLF2 mRNA level was assessed by qRT-PCR. Mean ± SEM, ns, nonsignificant; *P<0.05; ***P<0.0005, t-test, n=3. The inset shows a Western blot confirming ERK5 protein knockdown (average of 55% knockdown by densitometry from n=3 experiments). F. Same as in E but with and without BIX02189 (10 μM). Mean ± SEM, ns, non-significant; *P<0.05; **P<0.001, t-test, n=3. All qRT-PCR results were obtained from the average of 3 separate experiments, each performed in duplicate.
