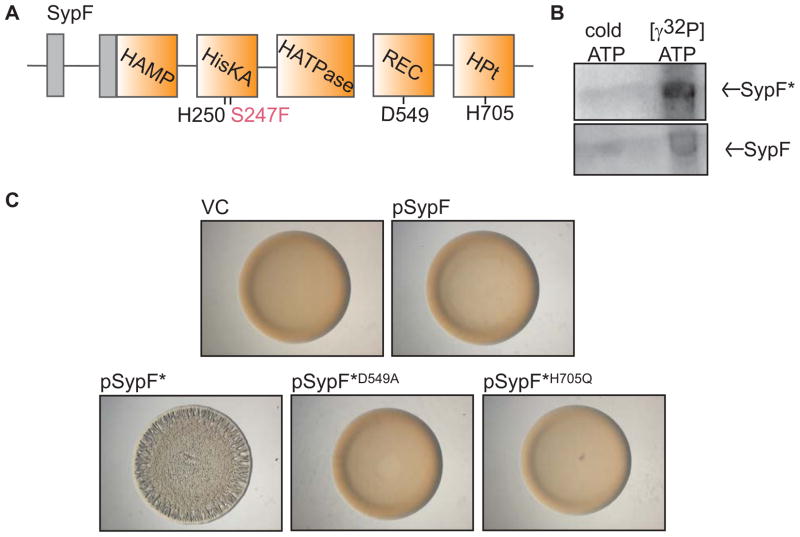
Figure 2. Function of SypF* as a SK.
(A) Cartoon of the predicted functional domains within SypF, including HAMP, HisKA, HATPase_c, REC, and HPt domains (orange boxes) as well as transmembrane regions (gray boxes) flanking a putative periplasmic loop. Conserved putative sites of phosphorylation are indicated below in black type. SypF* contains two mutations. The critical mutation, S247F, is indicated in pink type. (B) Autoradiograph of purified MBP-SypF* (above) and wild-type MBP-SypF (below) after incubation with unlabeled ATP or [γ-32P]-ATP. (C) Colony morphology of wild-type (WT) V. fischeri strain ES114 containing vector control (VC, pKV69) or various SypF and SypF* overproduction plasmids as follows: pSypF (pCLD54), pSypF* (pCLD29), pSypF*D549A (pANN61), and pSypF*H705Q (pANN62). Cultures of the indicated strains were spotted on agar plates and colony morphology was assessed after 24 h.