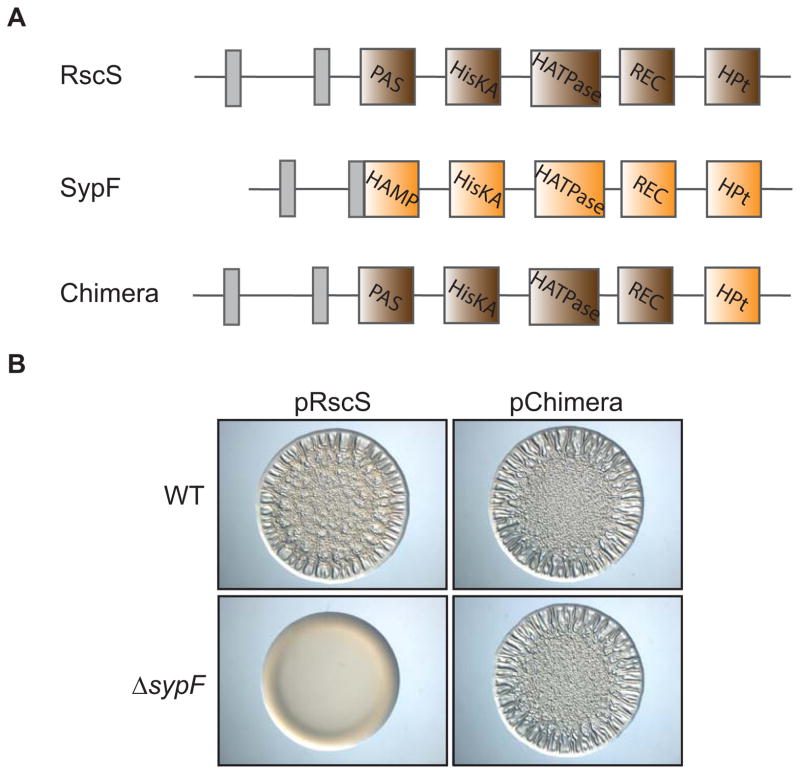
Figure 6. Interaction between RscS and SypF in the Syp biofilm pathway.
(A) Cartoon image comparing the predicted functional domains of RscS (brown: PAS, HisKA, HATPase_c, REC, Hpt), SypF (orange: HAMP, HisKA, HATPase_c, REC, HPt), and an RscS-SypF chimera that contains the N-terminal regions of RscS and the HPt domain of SypF. Grey boxes indicate transmembrane regions that flank a putative periplasmic domain. (B) Wrinkled colony formation of WT (ES114) or sypF deletion (KV5367) cells overproducing RscS (pARM7) or the RscS-SypF chimera (pANN69). Indicated strains were spotted and grown for 22 hours.