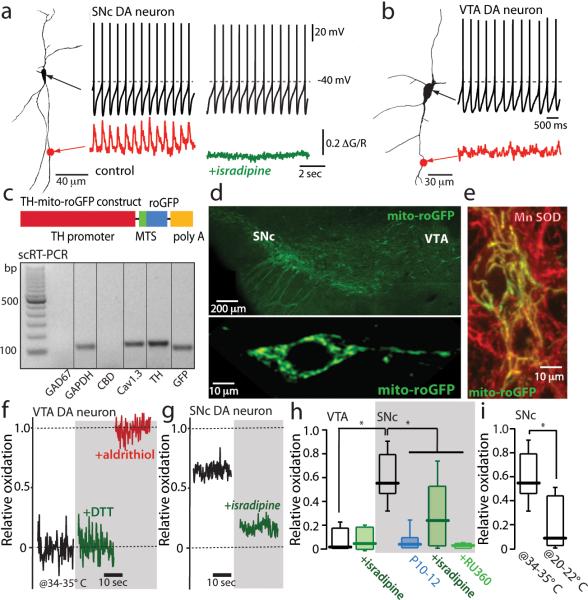
Figure 1. Calcium influx through L-type calcium channels during pacemaking increases mitochondrial oxidant stress in SNc dopaminergic neurons.
(a) Somatic whole cell recording from a SNc dopaminergic neuron (shown to the left as a projection image) in pacemaking mode. At the bottom of the panel, a 2PLSM measurement of dendritic Fluo-4 fluorescence (red trace) is shown. To the right are shown a similar set of measurements after application of isradipine; note the absence of a change in pacemaking rate but the loss of dendritic calcium transients (green trace)(n=10 neurons, P<0.05). (b) A similar set of measurements in a VTA dopaminergic neuron; these neurons consistently lacked dendritic calcium oscillations (n=6 neurons). (c) Schematic of the TH-mito-roGFP construct. Below the construct, single-cell RT-PCR analysis of mito-roGFP expressing SNc dopaminergic neuron showing expression of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and Cav1.3 calcium channel mRNA, but not calbindin (CBD) or GAD67 mRNA; similar results were obtained in all 5 neurons examined. (d) Top, a low magnification image of the mesencephalon of a transgenic TH-mito-roGFP mouse showing expression in SNc and VTA neurons. Bottom, a higher magnification image of a SNc neuron showing cytoplasmic but not nuclear labeling. (e) Overlay of Mn-SOD immunostaining (red) showing colocalization with mito-roGFP in cultured roGFP SNc neurons. (f) Mito-roGFP measurements from a VTA neuron; before (control, black trace), and after application of dithiothreitol (DTT) (green trace), and aldrithiol (red trace). Relative oxidation is plotted as described in Methods. (g) Mito-roGFP measurements from a SNc dopaminergic neuron (black trace) revealed a higher basal oxidation; treatment with isradipine diminished mitochondrial oxidation (green trace). (h) Left, box-plots summarizing mean redox measurements in control (n=9) and isradipine treated (n=5) VTA dopaminergic neurons; in control (n=14), isradipine (n=9) and Ru360 (n=8) treated SNc dopaminergic neurons; SNc neurons were significantly more oxidized than VTA neurons (P<0.05); both isradipine and Ru360 significantly reduced oxidation (P<0.05). SNc dopaminergic neurons from young mito-roGFP mice (P10-P12) were consistently less oxidized than adult neurons (P<0.05, n=8). (i) Box plots summarizing mean mito-roGFP measurements in SNc dopaminergic neurons in brain slices held at near physiological temperature (34-35°C) (n=14) and at room temperature (20-22°C) (n=5); oxidation was significantly less at room temperature (P<0.05). Statistical significance in all plots is shown by an asterisk and determined using a non-parametric test for comparing multiple groups (Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with Dunnet's post hoc test).