Figure 1. Proposed effects of protein intake and feeding pattern on muscle protein synthesis.
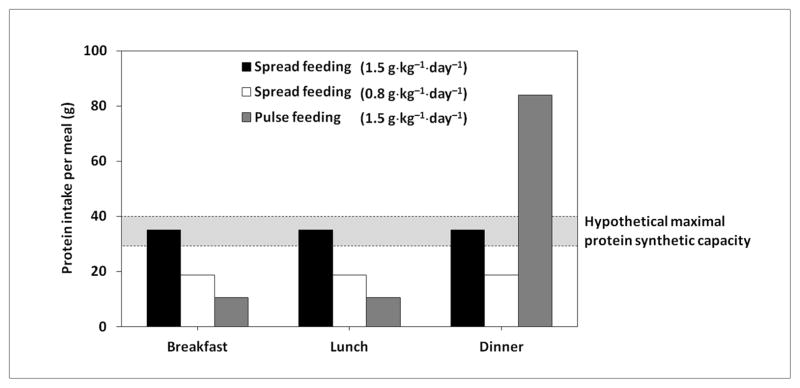
A protein intake of 0.8 g·kg−1·day−1 (56 g for a person weighing 70 kg) may not be sufficient to maximally stimulate muscle protein synthesis. The ingestion of 1.5 g·kg−1·day−1 of protein (105 g for a person weighing 70 kg) may differentially impact muscle protein synthesis depending on the feeding pattern. A spread feeding pattern, in which an equal amount of proteins is ingested at each meal, ensures a 24-h optimal stimulation of protein synthesis. A pulse feeding pattern, in which 80% of daily protein proteins is consumed in one meal and the remaining 20% is ingested in the other two meals, may not optimize the protein synthetic capacity. Adapted from Paddon-Jones D & Rasmussen BB, Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2009 (34).
