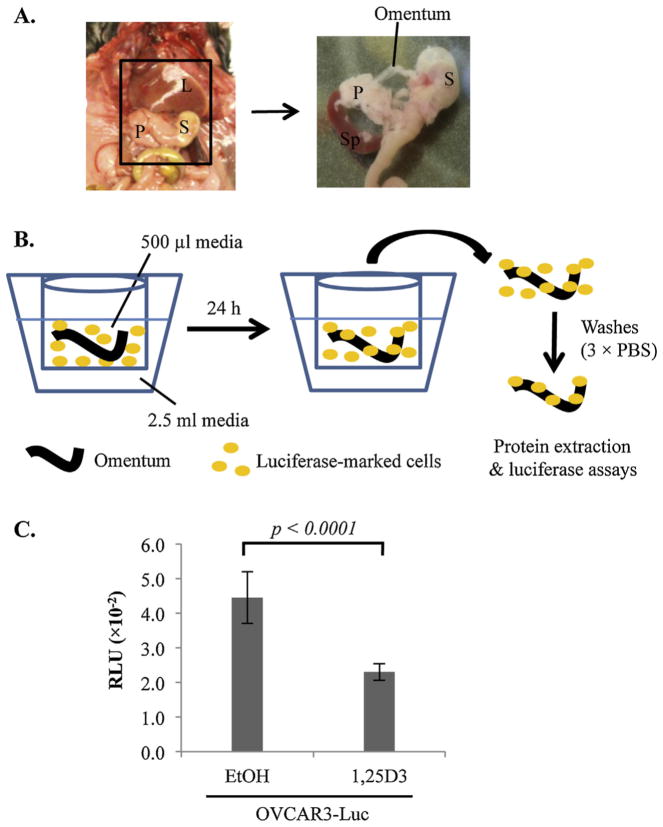
Fig. 2.
Suppression of EOC invasion into omentum by 1,25D3 through epithelial VDR in ex vivo assays. (A) A schematic diagram showing the location of the murine omentum in the peritoneal cavity between the liver (L), stomach (S), pancreas (P) and spleen (Sp). The right panel shows an enlarged view of the area with the omentum and its position relative to spleen, stomach and pancreas. The omentum was isolated by cutting the omental/pancreatic junction with a scissor. (B) Illustration of the ex vivo assay system of co-culturing mouse omenta and luciferase-marked human EOC cells. The omentum is cultured in the apparatus shown, consisting of a Millipore transwell insert containing 500 μl media, placed in a 12-well culture plate containing 2.5 ml media. (C) Suppression of EOC invasion into omenta by 1,25D3. OVCAR3-Luc cells were pretreated with EtOH or 10−7 M 1,25D3 for 6 days. 1 × 106 cells were co-cultured with the omentum for 24 h at 37 °C. For each data point, triplicate samples were analyzed. The experiments were reproduced twice.