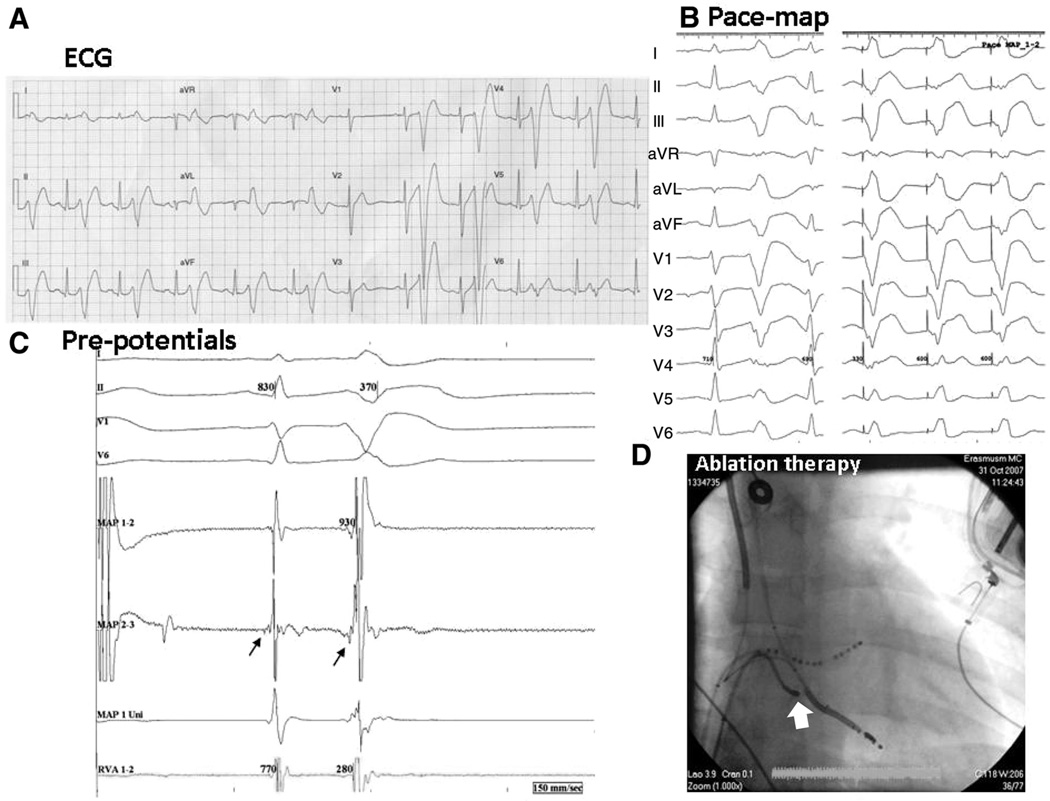
Figure 1. Radiofrequency ablation of idiopathic ventricular fibrillation in a DPP6 risk-haplotype carrier (patient E).
A, Early coupled ventricular extrasystoles (VESs) with a typical morphology in bigeminal pattern. B, left, Spontaneous VES; right, the pace map in the right ventricular (RV) apex. C, At the ablation site on the mapping ablation catheter, proximal recording (map 2–3) shows an early signal preceding the sinus beat, suggesting a Purkinje potential, which becomes clearer at the onset of a VES. D, Catheter position (arrow) at a successful ablation site (anteroposterior view). LV indicates left ventricle; and VF, ventricular fibrillation.