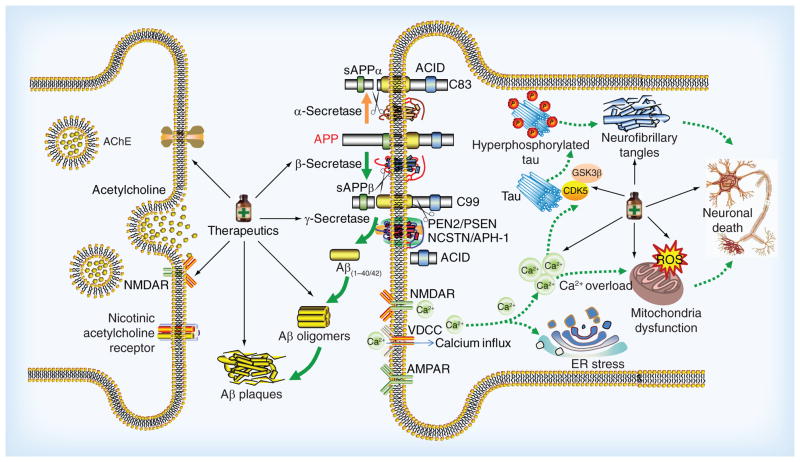
Figure 1. The complicated pathway and promising therapeutics in Alzheimer’s disease.
Aβ peptides are derived from APP. APP can be processed by amyloidogenic and nonamyloidogenic pathways which lead to different outcomes. In a nonamyloidogenic pathway, APP is initially cleaved by α-secretase to release sAPP-α and the left fragment is further processed by γ-secretase complex. In the amyloid pathway, APP is cleaved by β-secretase followed by γ-secretase complex to produce Aβ40/42, sAPP-β and AICD. Aβ42 has a high potential to aggregate to form toxic Aβ oligomers which cause the impairment of synapses and neurons. The Aβ oligomers increase the influx of Ca2+ and other different ions resulting in membrane depolarization. These results affect the function of different receptors and channels such as NAMDR, AMPAR and VDCC. In addition, the elevated Ca2+ can affect the modulation of tau-phosphorylating kinases such as GSK3β and CDK5, and result in the hyperphosphorylation of tau and the subsequent NFTs. Aβ also cause ER stress and mitochondria dysfunction by increase of ROS and Ca2+ dysregulation, which finally lead to dysfunction, degeneration and death of neurons. Based on the mechanisms and underlying targets associated with AD, some promising therapeutics designated by medicine bottles are under development, such as cholinergic drugs, amyloid-targeted therapies as well as drugs to target tau protein, mitochondrial function and neurotrophins.
Aβ: Amyloid β; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; AICD: Amyloid intracellular domain; AMPAR: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors; APP: Amyloid precursor protein; CDK5: Cell division protein kinase 5; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase 3β; NAMDR: N-methyl D-aspartate receptors; NFTs: Neurofibrillary tangles; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; sAPP-α: Soluble APP fragment α; sAPP-β: Soluble APP-β; VDCC: Voltage-dependent calcium channels.