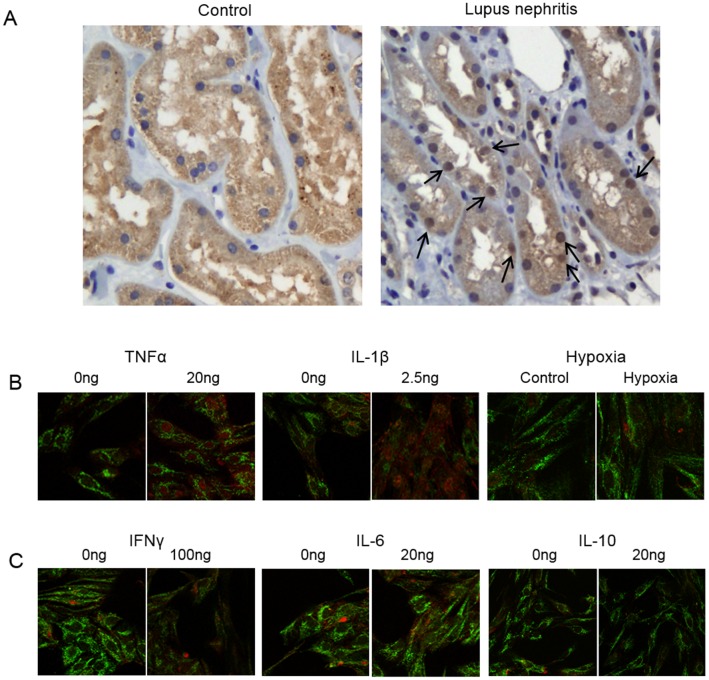
Fig 4. Sub-cellular location of DNaseI in lupus nephritis and in tubular cells stimulated with pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Immunohistochemistry analysis of renal DNaseI in a control human kidney sample demonstrated that DNaseI was predominantly localized in cytoplasm and not in nuclei (A, left panel). In human lupus nephritis the DNaseI was abundantly present in both cytoplasm and notably in nuclei (A, right panel, arrows point at positively stained nuclei). In human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTEC) DNaseI protein expression pattern was determined together with Trap 1 by confocal microscopy (B, green: anti-Trap 1 antibody, red: anti-DNaseI antibody), only the merged pictures are shown. While resting cells expressed DNaseI predominantly in cytoplasm, stimulation of RPTEC by TNFα and IL-1β resulted in nuclear translocation of the protein (B). Interestingly, stress by hypoxia also resulted in increased expression of the DNaseI protein but not in nuclear translocation (B). Nuclear translocation of DNaseI was notably not observed after stimulation of RPTEC with IFNγ, IL-6 or IL-10 (C).