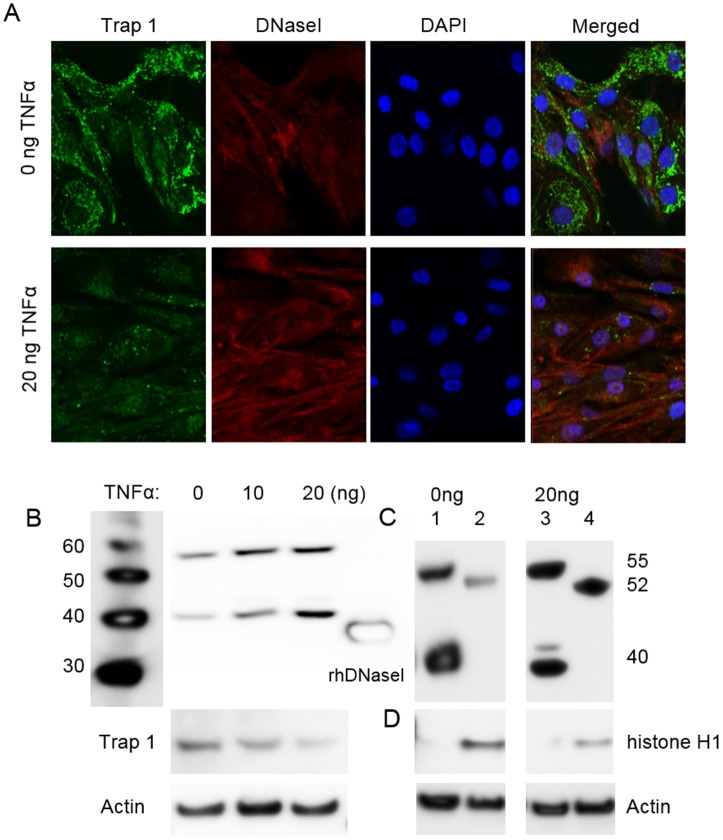
Fig 5. Cytoplasmic and nuclear DNaseI and Trap 1 expression in tubular cells after stimulation with TNFα.
Confocal microscopy of sham-stimulated human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells (RPTEC) (A, upper panels), and cells stimulated with 20ng/ml of TNFα for 48 hrs (A, lower panels) was performed by using anti-Trap1 antibodies (A, green) and by anti-DNaseI antibodies (A, red). No nuclear staining of DNaseI was observed in sham-stimulation of the cells (A, upper panels). After stimulation of RPTEC with TNFα, expression of DNaseI generally increased in staining intensity, and DNaseI translocated into the nucleus (A, lower panels). Nuclear location of DNaseI was confirmed by co-staining with DAPI (A, blue). The data demonstrate that DNaseI and DAPI were in confocus (violet in the merged picture, A, lower panel), thus confirming that DNaseI indeed was translocated to the nucleus. Correspondingly, by western blots both the 40 kDa and the 55 kDa bands increased in response to increasing TNFα stimulation (0, 10, 20ng/ml TNFα) (B). In the same cells, Trap 1 expression was reduced after TNFα stimulation, as determined by confocal microscopy (A, lower panels versus upper panels, green staining) and by western blot (B). Nuclear and cytoplasmic protein fractions were isolated from RPTEC after 48 hrs stimulation by TNFα (C). The 40 kDa and 55 kDa bands were detected in cytoplasmic fraction (C, lane 1), while weak 52 kDa band was observed in nuclear fraction of sham-stimulated RPTEC (C, lane 2). After 48 hrs stimulation with 20ng of TNFα, an increased DNaseI expression in cytoplasm (C, lane 3) and remarkably strong expression of the 52 kDa DNaseI in the nuclei was apparent (C, lane 4). Thus data from western blot analysis corresponded with data from confocal microscopy with respect to TNFα-induced nuclear translocation of DNaseI. Only nuclear fractions of RPTEC contained histone H1 protein as shown in D, confirming controlled separation of nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions in the cells. Actin was used as a loading control in all western blot analyses.