Fig. 6.
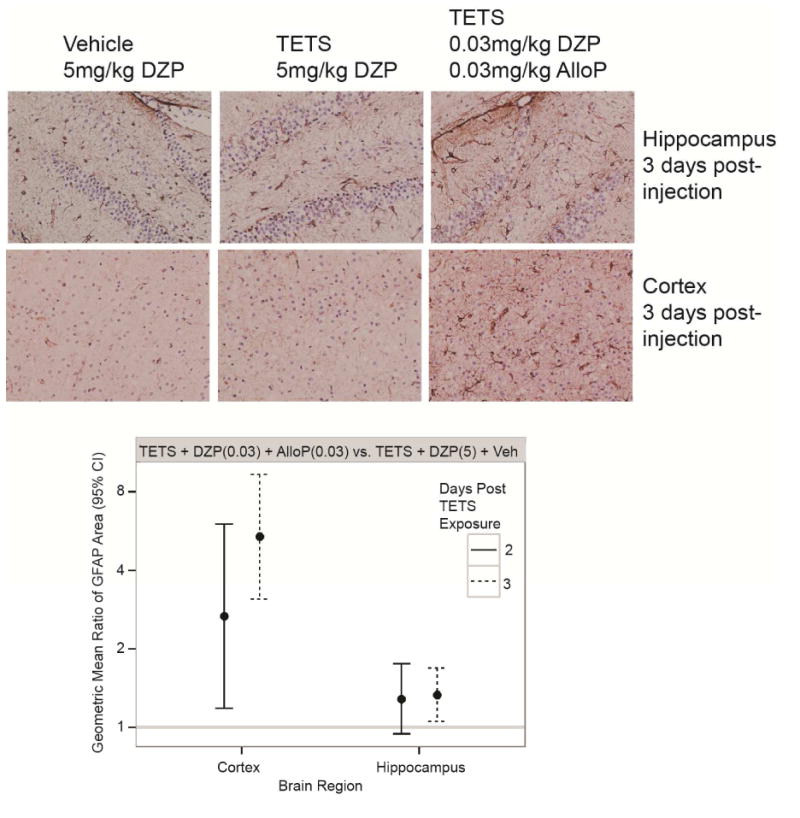
Combined treatment with low dose diazepam (DZP) and allopregnanolone (AlloP) increases reactive astrogliosis in TETS-intoxicated animals. Representative photomicrographs of GFAP immunoreactivity in the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of vehicle (saline) and TETS-intoxicated mice treated with high dose (5 mg/kg) DZP or a combination of low dose (0.03 mg/kg) DZP and AlloP at 3 d post-injection. The quantitative analyses of these data are represented by dot plots. Dots represent the geometric mean ratio of the area of GFAP immunoreactivity in TETS intoxicated animals treated with combined low dose DZP and AlloP versus TETS intoxicated animals treated with high dose DZP; bars represent 95% confidence intervals (n=3-6 animals per group with 4-7 sections per brain region per animal).
