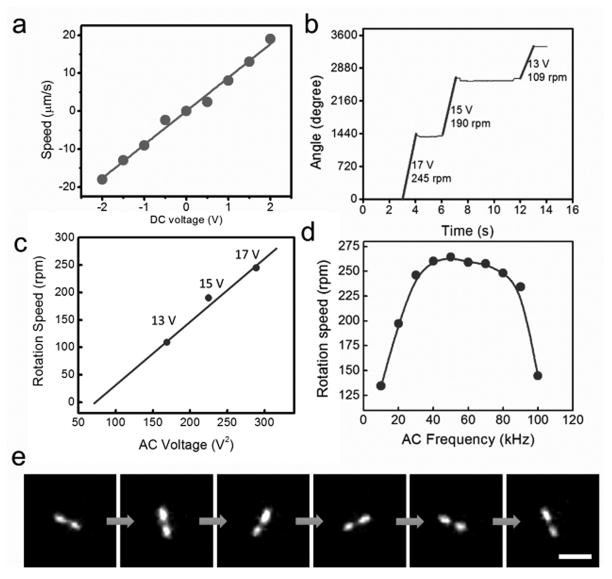
Figure 2.
(a) The transport speed of the plasmonic nanorotor increases with the applied DC voltages. (b, c) The rotation speed of nanomotor sensors increases linearly with V2 (20 kHz), (d) and depends on the applied AC frequency (15 V). (e) Snapshots (every 1/6 second) of a rotating nanomotor functionalized with NB imaged in the Raman mode. Note that the objective of the inverted microscope is underneath the rotating nanomotor. Thus the Raman image of the middle of the plasmonic nanomotor was blocked by the magnetic bearing. (Scale bar: 10 μm)