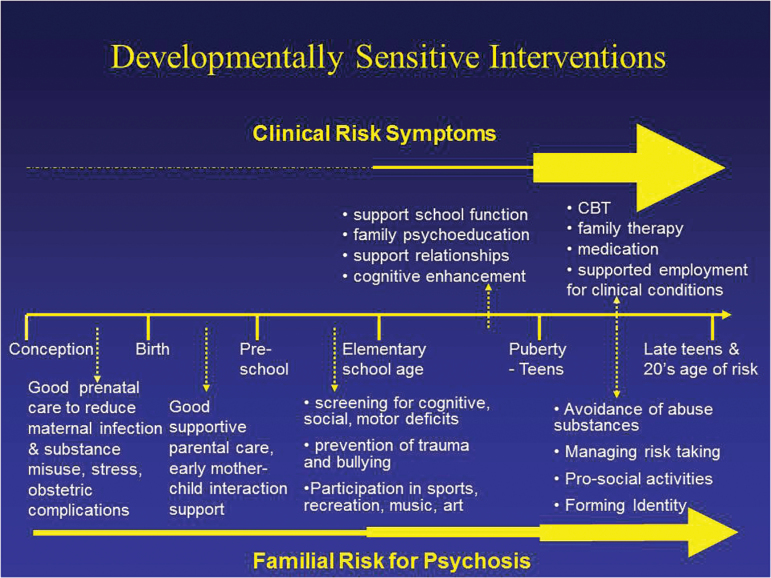
Fig. 1.
Phase specific early intervention & prevention strategies for clinical and familial high risk.
Clinical risk symptoms are contrasted with family risk for psychosis by depicting the greater likelihood of conversion to psychosis to occur in the clinical risk group by the larger yellow arrow. Interventions above the line for the clinical risk group begin around the end of elementary school reflecting the earliest period that prodromal symptoms are typically reported, whereas those below the line begin during pregnancy reflecting more of a primary prevention approach.