Figure 6. Proposed model of oncogene induced genomic instability in DLBCL.
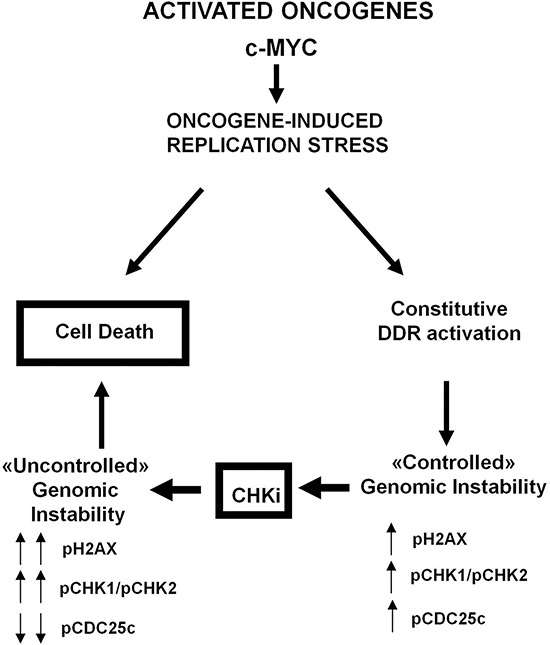
Constitutive expression of oncogenes such as MYC increases replicative stress and determines G1/S checkpoint activation, which in normal cells leads to apoptotic cell death. Aggressive B-cell lymphoma cells tolerate increased amounts of genomic instability by constitutive activation of the G2/M checkpoint/DDR pathway (ATM-ATR-CHK1-CHK2-CDC25c axis). Inhibition of the DDR pathway by CHK inhibitors (CHKi) acts as a synthetic lethal mechanism, leading to “uncontrolled” genomic instability and cell death.
