Figure 5. Knockdown of S100A6 activated CXCL14-induced apoptosis.
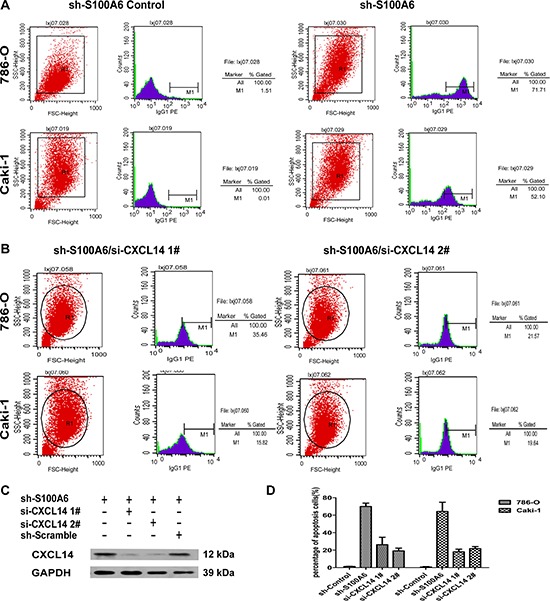
(A) The two-channel cell apoptosis analysis of shControl and shS100A6 in 786-O and Caki-1 cells detected the apoptosis in the screen eGFP live cells. (B) Further apoptosis analysis was performed in the shS100A6 cells which also knockdown the CXCL14, and the percentage of apoptosis were decreased. 1# and 2# were using the different CXCL14 si-sequence. (C) The transfection efficiency of si-CXCL14 1# and 2# in shS100A6 786-O cells were analysis by Western blot. (D) The percentage of apoptosis cells of shS100A6/si-CXCL14 1# and 2# were lower comparing to the untreated shS100A6 in both 786-O and Caki-1 cells. Data were expressed as mean ± SD and comparisons were performed using Student's t-test. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.05
