Figure 8. Effects of acetazolamide on Pgp activity, chemosensitivity and intracellular pH in chemoresistant cancer cells.
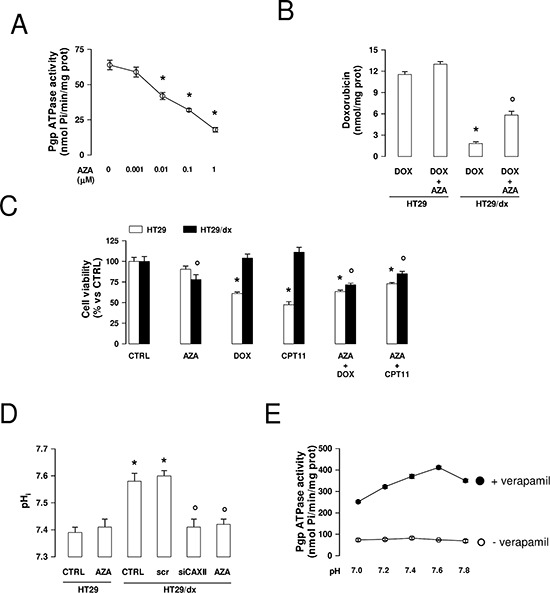
(A) Pgp-rich vesicles were extracted from membrane fractions of HT29/dx cells, then the Pgp ATPase activity was measured spectrophotometrically in the absence (0) or in the presence of increasing concentrations of acetazolamide (AZA), added during the assay. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 4). Versus 0: *p < 0.005. (B) HT29 and HT29/dx were incubated for 24 h with 5 μmol/L doxorubicin (DOX). When indicated, 1 μmol/L acetazolamide (AZA) was co-incubated. The intracellular doxorubicin retention was measured fluorimetrically. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 4). HT29/dx DOX cells versus HT29 DOX cells: *p < 0.001; HT29/dx DOX+AZA cells versus HT29/dx DOX cells: ° p < 0.005. (C) Cells were grown for 72 h in fresh medium (CTRL), or in medium containing 1 μM acetazolamide (AZA), 5 μmol/L doxorubicin (DOX), 1 μM irinotecan (CPT11), alone or in combination, then stained with neutral red dye. The absorbance of viable cells was measured spectrophotometrically. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 4). For HT29 cells, versus CTRL: *p < 0.001; for HT29/dx cells, versus CTRL: ° p < 0.05. (D) The intracellular pH (pHi) measurement was performed in duplicate (n = 4) on HT29 and HT29/dx cells untreated or treated with a non targeting scrambled siRNA (scr), with a CAXII-targeting specific siRNA pool (siCAXII) for 48 h, with 1 μmol/L acetazolamide (AZA) for 24 h. Significance versus HT29 cells: *p < 0.01; versus HT29/dx cells: ° p < 0.02. (E) The Pgp ATPase activity was measured spectrophotometrically in Pgp-rich vesicles extracted from HT29/dx cell membrane fractions, using buffers with different pH, in the absence (open circles) or presence (solid circles) of 10 μmol/L verapamil, chosen as a Pgp activator. Data are presented as means ± SD (n = 4).
