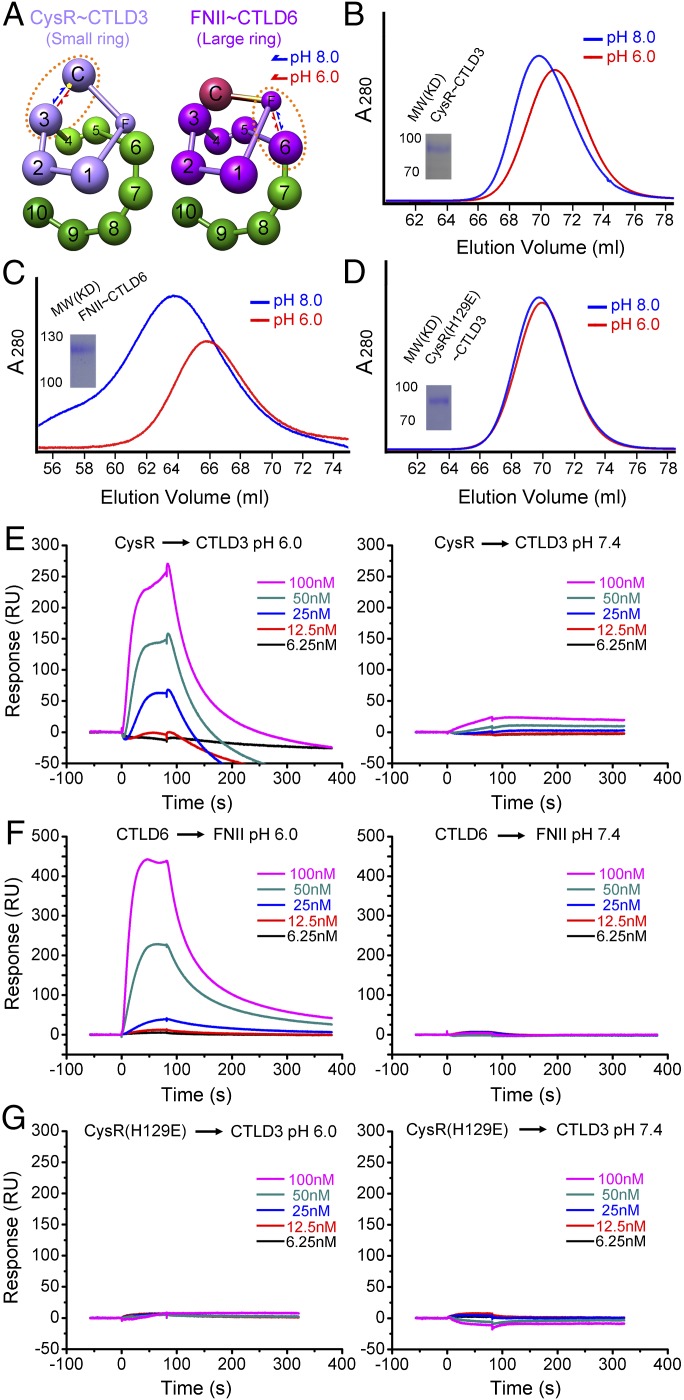
Fig. 3.
The mechanism of DEC205 conformational change. (A) The conformational change of the small ring (CysR∼CTLD3, light purple, Left) and the large ring (FNII∼CTLD6, dark purple, Right) of DEC205 between acidic and basic pH. The approximate position of H129 is shown as a yellow dot. The domains involved in the intramolecular interactions are circulated by the brown dotted lines. (B) SEC profiles of the small ring at pH 6 and pH 8. (C) SEC profiles of the large ring at pH 6 and pH 8. (D) SEC profiles of the small ring H129E mutant at pH 6 and pH 8. (E) Sensorgrams for the interactions of CysR with CTLD3 at acidic (Left) and basic (Right) conditions. (F) Sensorgrams for the interactions of CTLD6 with FNII at acidic (Left) and basic (Right) conditions. (G) Sensorgrams for the interactions of CysR(H129E) with CTLD3 at acidic (Left) and basic (Right) conditions.