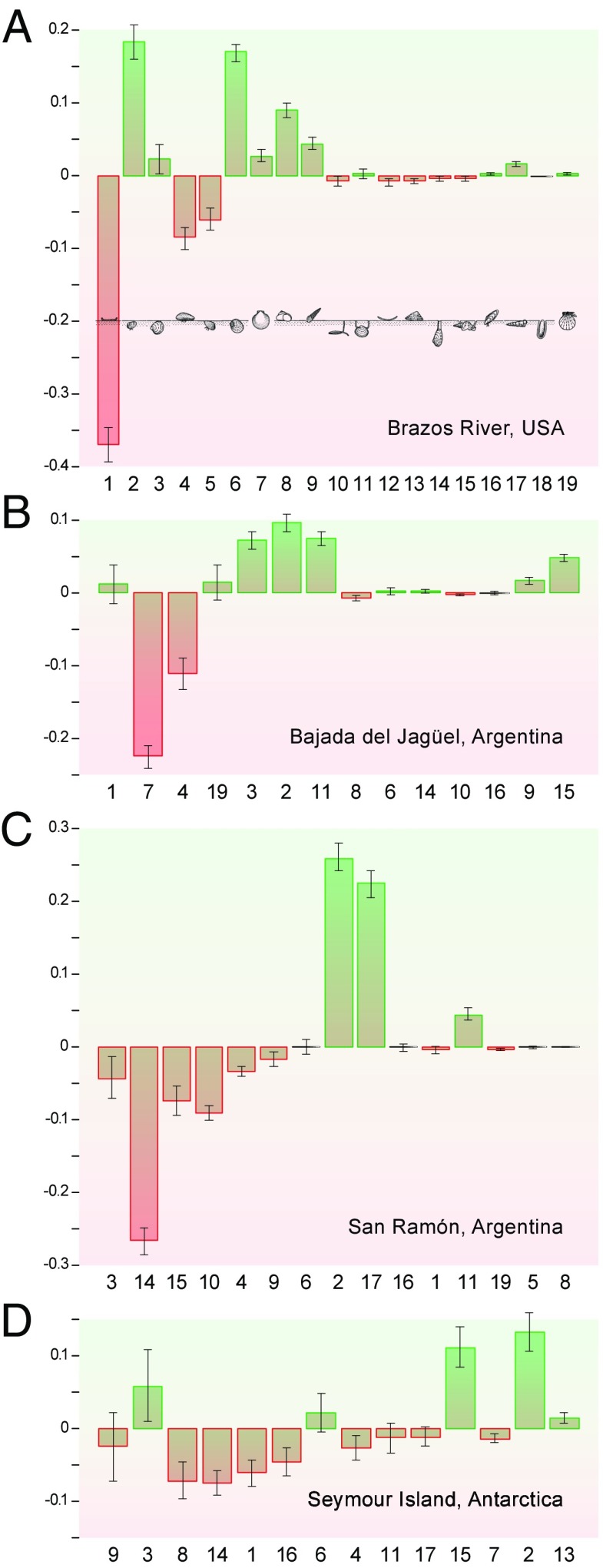
Fig. 1.
Changes in the proportional abundance of modes of life (MOLs 1–19) represented in marine molluscan assemblages across the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary. The four analyzed sites (A–D) are arranged from north (A) to south (D) and also reflect increasing distances from the Chicxulub impact site. Modes of life are rank ordered according to their preextinction abundance, decreasing from Left to Right. Negative values indicate proportionally declining modes of life and positive values, expanding modes of life across the KPB. Error bars represent the summed SEs of pre- and postextinction proportions. 1, epifaunal, stationary, cemented, suspension feeders; 2, shallow infaunal, motile, deposit feeders; 3, shallow infaunal, facultatively motile, unattached, suspension feeders; 4, epifaunal, stationary, byssate, suspension feeders; 5, shallow infaunal, facultatively motile, byssate, suspension feeders; 6, shallow infaunal, motile, carnivores; 7, epifaunal, facultatively motile, unattached, suspension feeders; 8, epifaunal, motile, herbivores; 9, epifaunal, motile, carnivores; 10, deep infaunal, facultatively motile, surface deposit feeders; 11, deep infaunal, facultatively motile, chemosymbiosis; 12, epifaunal, stationary, unattached, suspension feeders; 13, epifaunal, facultatively motile, herbivores; 14, deep infaunal, facultatively motile, suspension feeders; 15, shallow infaunal, motile, surface deposit feeders; 16, semiinfaunal, stationary, byssate, suspension feeders; 17, shallow infaunal, motile, suspension feeders; 18, infaunal, stationary, boring, suspension feeders; and 19, epifaunal, facultatively motile, byssate, suspension feeders.