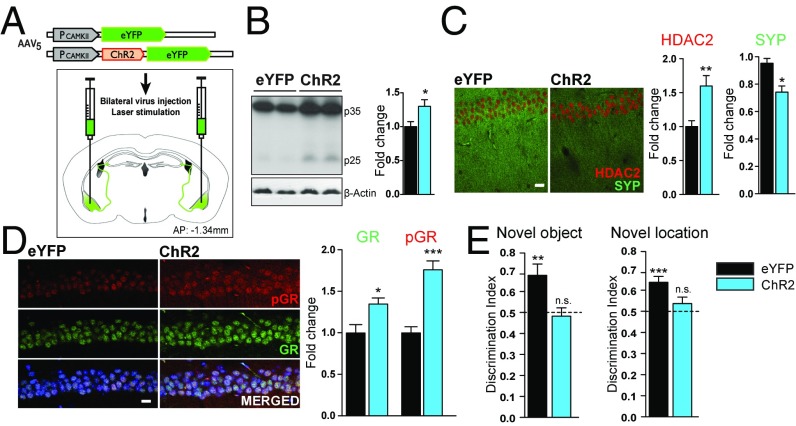
Fig. 3.
BLA activation is sufficient to reproduce repeated stress-induced hippocampal molecular changes and learning and memory deficits. (A) Schematic of the AAV5-CaMKIIa-eYFP and AAV5-CaMKIIa-ChR2-eYFP constructs, mode of virus administration, and fiber optic placement. (B) Effect of BLA photostimulation on p25 generation in the hippocampus (n = 5 per group; unpaired t test). (C and D) Representative immunohistochemical images and quantitative analysis of HDAC2 and Synaptophysin (C) and GR and pGR (D) expression levels in the dorsal hippocampal CA1 subregion from eYFP and ChR2 mice (n = 5 per group; unpaired t test) (HDAC2 and pGR in red; Synaptophysin and GR in green; DAPI in blue). (E) Effect of optogenetic BLA activation on performance in novel object recognition and novel location recognition behavioral tasks (n = 10 CON mice and 7 ChR2 mice; one-tailed t test). Values are mean ± SEM. n.s., nonsignificant; P > 0.05; *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001. (Scale bars: 20 µm.)