Abstract
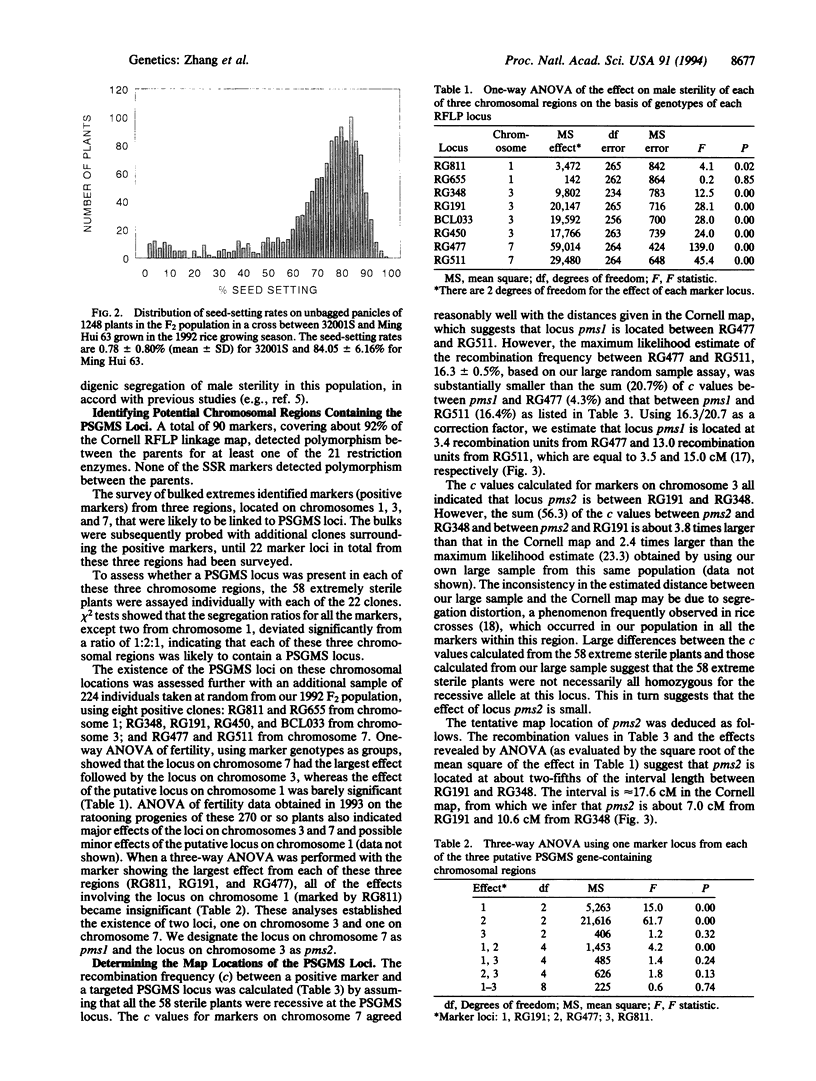
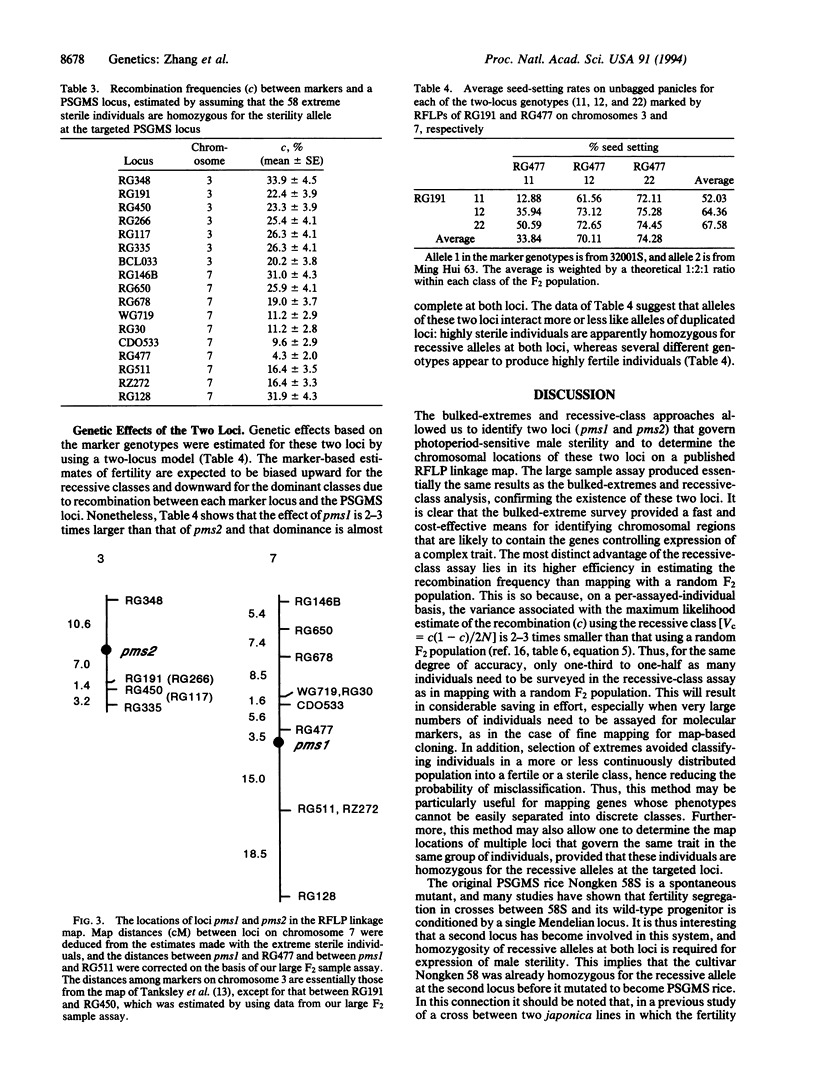
Photoperiod-sensitive genic male sterile (PS-GMS) rice has a number of desirable characteristics for hybrid rice production. In this study we made use of a published rice genetic linkage map to determine the locations of PSGMS genes and we have characterized the effects of these genes on sterility by using molecular markers. A two-step approach was designed for mapping the genes: (i) identifying possible PSGMS gene-containing chromosome regions with bulked DNA from extreme fertile and extreme sterile plants of a very large F2 population and (ii) determining the map locations of the genes in extreme sterile individuals. We show that this mapping method is much more cost effective and statistically efficient than using a random sample of an F2 population. We identified two chromosomal regions each containing a PSGMS locus, one designated pms1 on chromosome 7 and one designated pms2 on chromosome 3. The existence of these two loci was confirmed by a large sample assay and with data on rationing progenies of the F2 plants. A marker-based analysis shows that the effect of pms1 is 2-3 times larger than that of pms2 and that dominance is almost complete at both loci. Implications in the breeding of PSGMS rice lines are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Michelmore R. W., Paran I., Kesseli R. V. Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9828–9832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saghai-Maroof M. A., Soliman K. M., Jorgensen R. A., Allard R. W. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):8014–8018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.8014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. S., Tanksley S. D. Abundance, polymorphism and genetic mapping of microsatellites in rice. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Oct;241(1-2):225–235. doi: 10.1007/BF00280220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]