Figure 10. Model for the mechanism of action of HDAC1,2-selective inhibitor in EZH2GOF DLBCL cells.
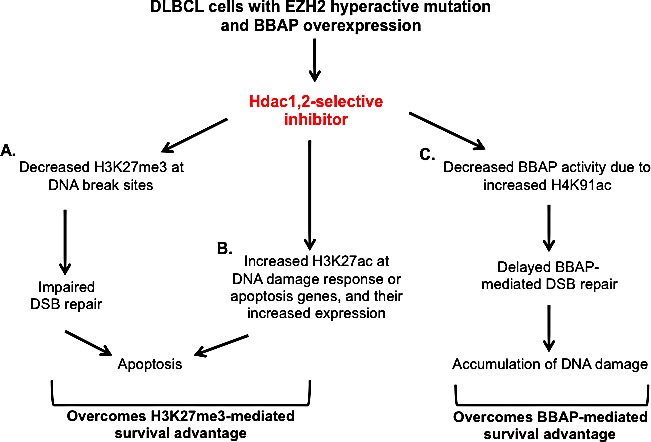
A: HDAC1,2 selective inhibition decreases H3K27me3 at break sites to impair DSB repair and activate DNA damage response. B: HDAC1,2 inhibition increases H3K27ac at DNA damage response genes to increase their transcription. A and B together overcomes the survival advantage provided by increased H3K27me3 in these EZH2GOF DLBCL cells. C: HDAC1,2 inhibition increases H4K91ac and decreases H4K91 monoubiquitination following doxorubicin treatment. This results in a defective 53BP1 recruitment to damage sites and defective repair of doxorubicin-induced breaks. Hence, HDAC1,2 inhibition overcomes BBAP-mediated chemoresistance following doxorubicin treatment in DLBCL cells with EZH2 hyperactive mutation.
