Figure 3. Canertinib and afatinib induced down regulation of cell survival and cell cycle related protein is partly responsible for decreased cell proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells.
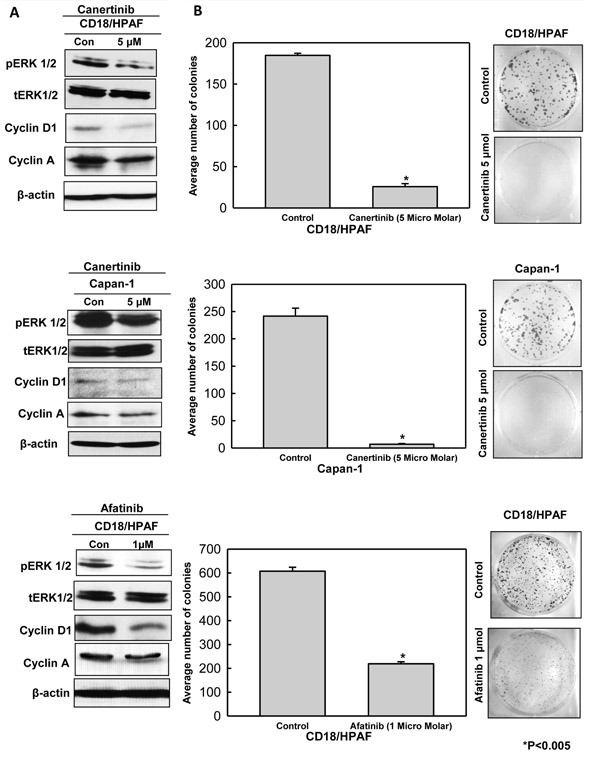
(A). Treatment of pancreatic cells (CD18/HPAF and Capan-1) resulted in down regulation of major proteins responsible for cellular proliferation and cell cycle regulation. Immunoblotting analysis with specific antibodies toward phospho-ERK1/2 and Cyclin D1 and Cyclin A was carried out on whole cell lysates of pancreatic cancer cells incubated in the presence or absence of canertinib and afatinib for 24 hours. The total ERK remains unchanged in control and treatment conditions. Beta actin was used as the loading control. (B). Influence of canertinib and afatinib on cell survival and viability was functionally determined by colony forming assay. Colony forming assay was done in CD18/HPAF (0.1-0.3×104) and Capan-1(0.1×104) pancreatic cancer cells with indicated concentrations of canertinib, afatinib and DMSO treatment. Six well plates were seeded with above mentioned pancreatic cancer cell density in complete medium. After 48 hours of incubation, the cells were washed with PBS and supplement with inhibitors or vehicle in complete medium (10% DMEM). After a period of 10 days of incubation the cells were fixed with 100% ice cold methanol and stained with 0.4% crystal violet in methanol. Representative images show significant reduction in the number of colonies in the canertinib and afatinib treated cells as compared to vehicle or untreated control cells.
