Figure 3. HIV-1 Nef induces NF-κB p65 translocation as well as the phosphorylation of IκBα and IKK.
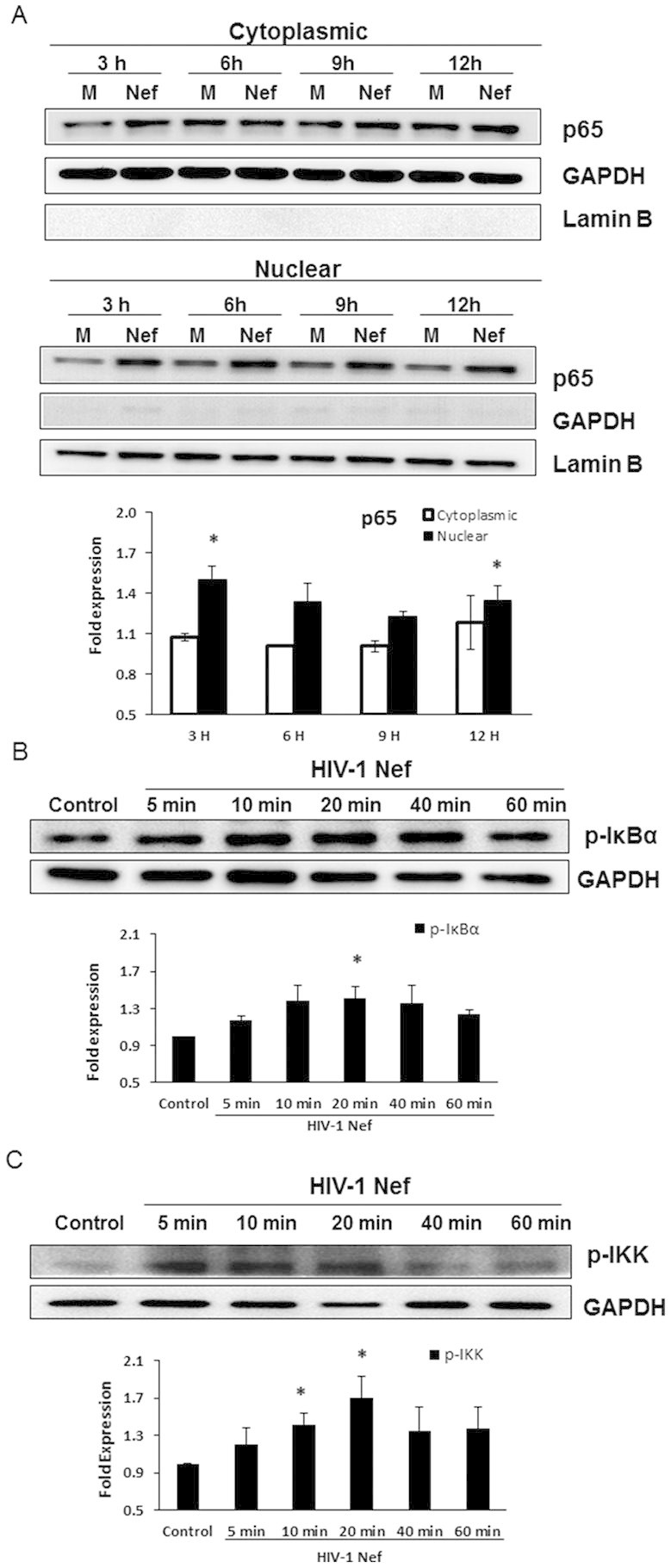
7 × 105 SVGA astrocytes were seeded in 6-well plates and were transfected with a plasmid encoding HIV-1 Nef using Lipofectamine 2000™. The transfection start time was considered time 0. The cells were harvested at the indicated times for isolation of cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins. The expression levels of p65 were determined in the cytosol and nucleus by western blotting. The figure shows one set of data that is representative of 3 independent experiments. Levels of p65 were quantified by spot densitometry and are presented as mean ± SE of 3 independent experiments. The fold expression of p65 was calculated relative to that of the mock-transfected wells at each individual time point (A). GAPDH was used as a loading control for cytoplasmic extracts and Lamin B was used as a loading control for nuclear extracts. In separate experiments, astrocytes were seeded in 6-well plates and were treated with recombinant HIV-1 Nef at the concentration of 20 nM. The cells were harvested at the indicated times for preparation of whole cell lysates followed by western blotting for determination of p-IκBα and p-IKK levels. The figure shows one set of data that is representative of 3 independent experiments. Levels of phosphorylated-proteins were quantified by spot densitometry and are presented as mean ± SE fold vs. control of 3 independent experiments (B–C). GAPDH was used as a loading control. Statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with an LSD post-hoc test in which * represents p-value ≤ 0.05 and ** represents p-value ≤ 0.01.
