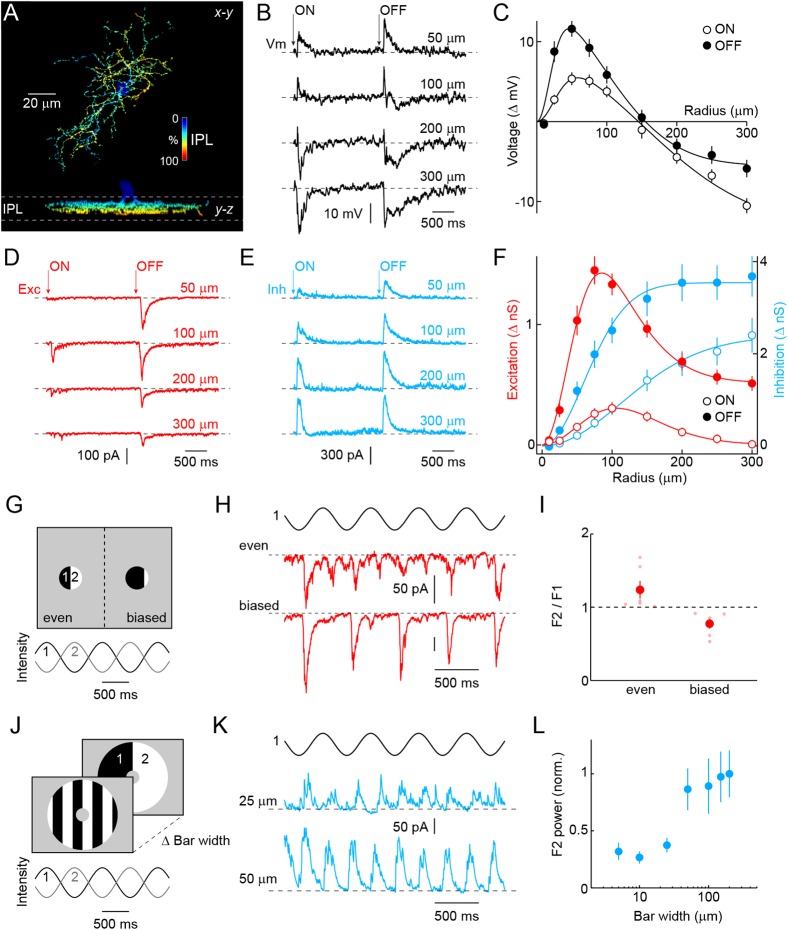
Figure 1. Morphology and receptive field properties of VG3-ACs.
(A) Orthogonal maximum intensity projections of a confocal image stack through a representative VG3-amacrine cells (ACs) labeled in VG3-CreERT2 Ai9 mice. The fluorescent signal is colored to reflect depth in the inner plexiform layer (IPL). Inset bar graph shows the mean ± SEM territory size of VG3-ACs (n = 39) measured as the area of the smallest convex polygon to encompass their arbors in a z-projection. (B, D, E) Representative voltage (B, black), excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) (D, red), and inhibitory postsynaptic current (IPSC) (E, blue) responses to a stimulus in which luminance in a circular area of varying size is square-wave modulated (2 s ON, 2 s OFF, transitions indicated by ‘arrows’). Stimuli were presented in pseudorandom order centered on the soma of the recorded cell. Each response trace is annotated with the radius of the stimulus eliciting it. The resting membrane potential of VG3-ACs in our recordings was −38 ± 1.2 mV (n = 26). (C, F) Summary data of the spatial ON (open circles) and OFF (filled circles) sensitivity profiles of VG3-ACs for voltage responses (C, black, n = 26) and excitatory (F, red, n = 38) and inhibitory (F, blue, n = 38) conductances. Solid lines show fits of Difference-of-Gaussian (for voltage and excitation) and single Gaussian (for inhibition) models to the data. Receptive field diameters determined from fits to voltage responses were: ON-center 73.4 ± 8.5 μm, OFF-center 40.9 ± 4.2 μm, p < 0.002, ON-surround 290.2 ± 25.5 μm, OFF-surround 213.3 ± 11.3 μm, p < 10−3. Receptive field diameters for excitatory inputs were: ON-center 137 ± 15.8 μm, OFF-center 83.1 ± 10.2 μm, p < 0.005, ON-surround 206.4 ± 14.3 μm, OFF-surround 189.8 ± 23.2 μm, p > 0.4. Diameters of inhibitory center-only receptive fields were: ON 258 ± 24.7 μm, OFF 148.2 ± 12.3 μm, p < 10−4. Response amplitudes to OFF stimuli exceeded those to ON stimuli for voltage (at 100 μm, p < 10−9), excitation (at 100 μm, p < 10−11), and inhibition (at 100 μm, p < 10−5). (G) Schematic illustration of split-field stimuli. The receptive field center is divided evenly (left) or in a biased manner (right) into two regions in which intensity is modulated by phase-shifted sine waves. (H, I) Representative EPSC traces and summary data (n = 6, p < 0.05) for even (top) and biased (bottom) split-field stimulation. (J) Schematic illustration of counter phase stimulation of surround regions. The receptive field surround is divided in bars of different size and their intensity is modulated by phase-shifted sine waves. (K) Representative IPSC traces to counter phase stimulation of bars of 25 μm (middle) and 50 μm (bottom) widths. (L) Summary data illustrating change in F2 power of inhibition as a function of bar widths. See also Figure 1—figure supplement 1 and Figure 1—figure supplement 2.