Figure 4. Effect of HBC on androgen-stimulated AR.
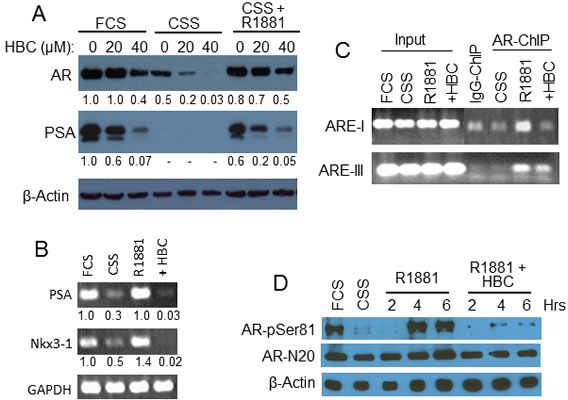
A and B) HBC inhibits androgen-stimulated AR activity. Exponentially growing LNCaP cells (FCS) were hormone-deprived (CSS) and stimulated with 2 nM R1881 in the absence or presence of HBC for 24 hours. AR, PSA and β-actin protein (A) and PSA, NKX3.1, and GAPDH mRNA levels (B) were determined by Western blot and RT-PCR, respectively. Cells treated with 40 μM HBC were used for RT-PCR analysis. Band densities were determined by using the ImageJ program and β-actin- (A) and GAPDH- (B) normalized relative band densities are presented. C) HBC inhibits AR association with PSA- AREs. Hormone-deprived LNCaP cells were treated with 2 nM R1881 in the presence of 40 μM HBC, chromatin-immunoprecipitates were prepared using ant-AR-N20 antibodies (AR-ChIP), and DNA was purified from AR-ChIP and subjected to PCR analysis. ChIP prepared using purified IgG (IgG-ChIP) served as a negative control. Input represents 10% of chromatin used for Immunoprecipitation. D) HBC inhibits phosphorylation of AR Serine 81 residue. Cell extracts prepared from hormone-deprived cells stimulated with R1881 (2 nM) in the presence of HBC (40 μM) for 2, 4, or 6 hours were subjected to Western blot analysis using antibodies against AR-pSer81, AR-N20 and β-actin. All experimental procedures are as described in Materials and Methods. Data in each panel is representative of 2 or more independent experiments.
