Fig 7.
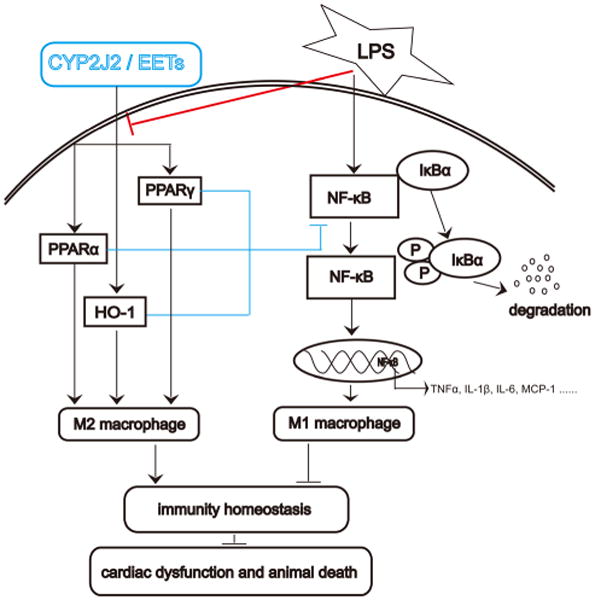
Schematic of mechanisms on CYP2J2/EETs mediated macrophage polarization in response to LPS-induced inflammation and cardiac dysfunction. A stop (┴) indicates inhibitory or blocking effects, and an arrow (↓) indicates increased or enhanced effects. LPS-treatment induced M1 macrophage polarization via NF-κB activation. Phosphorylation of IκB resulted in its dissociation from the transcription factor NF-κB, allowing NF-κB to translocate to the nucleus and participate in transcription of genes involved in inflammation. Ultimately, LPS-treatment induced cardiac dysfunction and animal death. CYP2J2 overexpression or CYP2J2 derived EETs regulates M2 macrophage polarization via up-regulation on PPARα/γ and HO-1, down-regulation on NF-κB signaling pathway, which maintains immunity homeostasis and improves cardiac dysfunction and survival in sepsis mice.
