Figure 5.
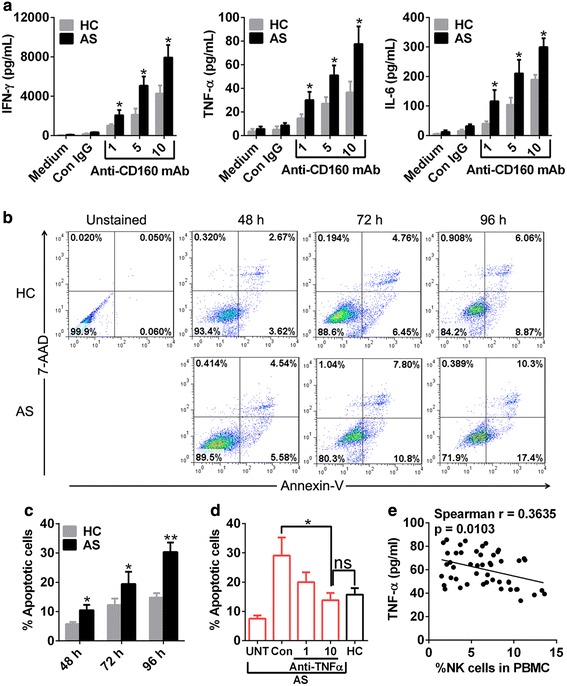
CD160 engagement triggers secretion of inflammatory cytokines and subsequent NK cell death. a Engagement of CD160 receptor on NK cells from AS patients (n = 5) and HC (n = 5) was conducted by using an anti-CD160 agonistic mAb at serial concentrations indicated in figures. Treatments with medium and IgG1 isotype control were used as controls. Sixteen hours later, supernatants were collected and assayed for the production of IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-6. b, c NK cells from AS patients and HC were treated as above and their apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/7-AAD staining 48, 72 and 96 h later with apoptotic cells defined as Annexin V+ cells (c). The representative dot plots were shown in b. d Engagement of CD160 receptor on NK cells from AS patients were performed in the presence of control (10 µg/ml) or TNF-α-neutralizing (1 and 10 µg/ml) mAb and their apoptosis was determined by Annexin V/7-AAD staining 96 h later. Untreated NK cells from AS patients (UNT, no CD160 engagement) and treated NK cells from HC (CD160 engagement without neutralizing mAb) were used as controls. e The correlation of serum TNF-α with the percentage of NK cells in PBMCs with each dot presenting one subject. In these experiments, the purity of NK cells we used was >95% as determined by flow cytometry (Additional file 1: Figure S1). Data are expressed as mean ± SD of five AS patients and HC with each case triplicates (a) or representative of two independent experiments (c, d). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, student t test (a, c, d) and spearman correlation test (e).
