Figure 6.
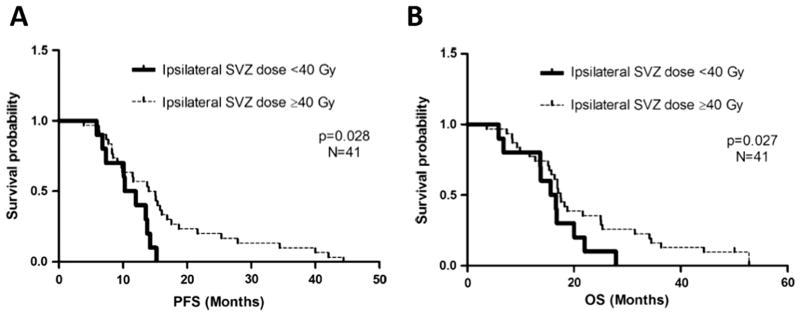
Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) improve in the subgroup of patients that underwent gross total resection and received increased dose to SVZ in Chen et al.9 (A) PFS by ipsilateral subventricular dose in gross total resection patients (n = 41). PFS in patients whose ipsilateral subventricular zone (SVZ) received less than 40 Gy was significantly different from that in those who received a dose of 40 Gy or greater as measured by median PFS of 10.3 vs 15.1 months (95% CI: 7.4–13.2 months) and log-rank test (PZ.023), as well as adjusted hazard ratio for PFS (2.60) (PZ.028). (B) Overall survival (OS) by ipsilateral subventricular dose in gross total resection patients (n = 41). OS in patients whose ipsilateral subventricular zone (SVZ) received less than 40 Gy was significantly different from those who received a dose of 40 Gy or greater as measured by median overall survival of 15.6 vs 17.5 months (95% CI: 11.3–19.9 months) and adjusted hazard ratio for progression-free survival (2.60) (PZ.027).
