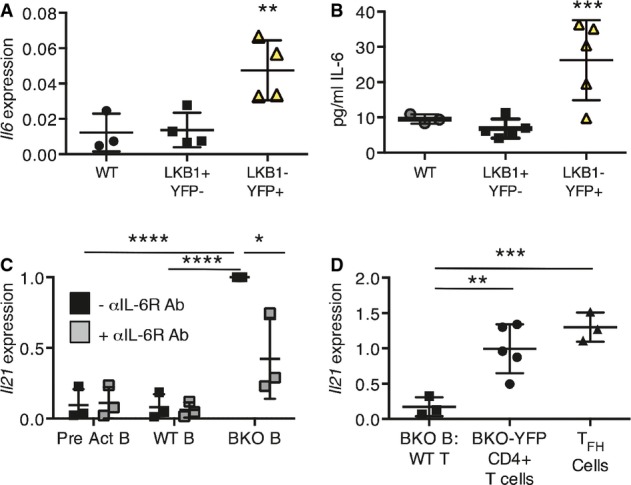
qRT–PCR for Il6 expression, relative to 36b4 expression, in CD43-depleted splenic B cells from WT-YFP (n = 3), and LKB1+YFP−- (n = 4) and LKB1−YFP+- (n = 4) sorted CD19+ splenic B cells from BKO-YFP mice. **P = 0.0098 by one-way ANOVA.
IL-6 secreted by WT-YFP (n = 3), and LKB1+YFP− (n = 5) and LKB1−YFP+ (n = 5) CD19+ splenic B cells from BKO-YFP mice during 24 h in culture. ***P = 0.0047 by one-way ANOVA.
CD4+CD62L+ naïve T cells were co-incubated with anti-CD3 Ab and WT B cells pre-activated for 24 h, WT B cells, or B cells from BKO mice, with or without anti-IL-6R Ab for 48 h. qRT–PCR for induced Il21 expression, relative to 36b4 expression, and normalized to the induction of Il21 expression in BKO B-cell co-culture, is shown. Three independent experiments; ****P = 0.0002 and 6.5E-05, *P = 0.024, respectively, by two-tailed, unpaired Student's t-test.
qRT–PCR analysis of Il21 expression, relative to 36b4 expression, by CD4+CD62L+ T cells co-incubated with anti-CD3 antibody and B cells from BKO-YFP mice for 48 h, CD4+ T cells from BKO-YFP mice, or sorted TFH cells from LCMV-infected WT mice. Three independent experiments (co-culture) or 3 biological replicates; **P = 0.009 and ***P = 0.0014 by two-tailed, unpaired Student's t-test.
Data information: Mean ± s.d.