Figure 1.
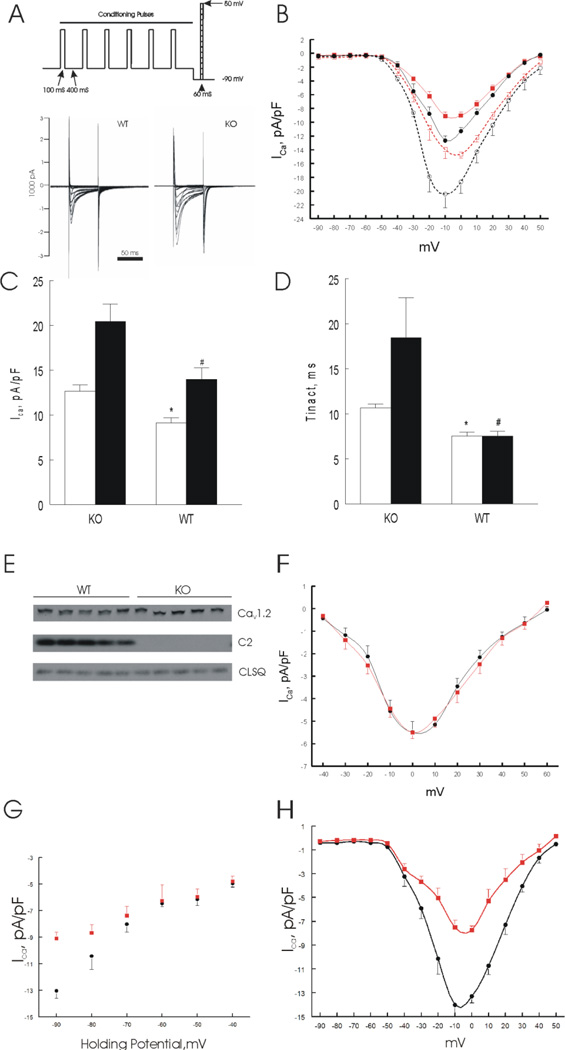
Phospholemman (PLM) regulates L-type Ca2+ current (ICa) in adult mouse left ventricular (LV) myocytes. Myocytes were isolated from LV of wild-type (WT) and phospholemman knockout (KO) mice and ICa was measured on the same day. A. Voltage-clamp protocol and representative ICa traces from WT and KO myocytes. B. Current-voltage (I-V) relationship of ICa from WT (■; n=14) and KO (●; n=12) myocytes at baseline; and after stimulation with 1 µM isoproterenol (□ WT, n=7; and ○ KO, n=5). Holding potential was −70 mV and stepped to −90 mV before arrival of test pulses. Error bars are not shown if they fall within the boundaries of the symbols. C & D. Peak ICa amplitudes and time constants of inactivation (τinact) (at −10 mV) of KO and WT myocytes, both in the absence (open bars) and presence (solid bars) of 1 µM isoproterenol.*p<0.0002, WT vs. KO; #p<0.008, WT-Iso vs. KO-Iso. E. LV homogenates were prepared from WT and KO mice and probed for α1-subunit of L-type Ca2+ channel (Cav1.2) and phospholemman (C2); calsequestrin (CLSQ) was used as loading control. There were no differences (p<0.8) in Cav1.2 expression between WT (0.92 ± 0.02) and KO myocytes (0.94 ± 0.04 arbitrary units)(n=5 each). F. I-V relationship of ICa from WT (■; n=6) and KO (●; n=4) myocytes at baseline. Holding potential (−70 mV) was stepped to −40 mV before arrival of test pulses. Error bars are not shown if they fall within the boundaries of symbols. Note the difference in ordinate scales between B and F. G. ICa amplitudes at −10 mV elicited at holding potentials from −90 to −40 mV for WT (■; n=3 to 15) and KO (●; n=3 to 15) myocytes at baseline. Two-way ANOVA indicates significant group (WT vs. KO; p<0.0001), holding potential (p<0.0001) and group × holding potential interaction (p<0.0001) effects, indicating that varying the holding potential significantly affected the inherent differences in ICa between WT and KO myocytes. H. Baseline current-voltage (I-V) relationship of ICa ilicited at holding potential of −90 mV from WT (■; n=4) and KO (●; n=4) myocytes in the presence of 50 µM TTX.