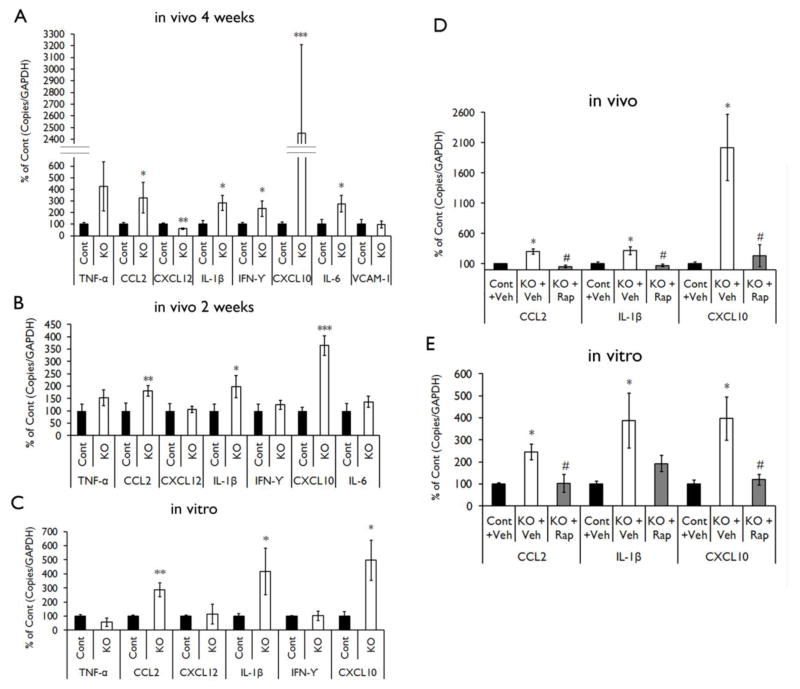
Figure 1. Proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines are up-regulated in Tsc1GFAPCKO mice and inhibited by rapamycin.
mRNA expression of cytokines and chemokines was evaluated by real-time quantitative RT-PCR in the brains or cultured astrocytes from Tsc1GFAPCKO and control mice. (A) The mRNA levels of CCL2, IL-1β, IFN-γ, CXCL10 and IL-6 were increased in four-week old Tsc1GFAPCKO mice compared with control mice, but CXCL12 was decreased (n = 8–10 mice/group). (B) The mRNA levels of CCL2, IL-1β and CXCL10 were increased in two-week old Tsc1GFAPCKO mice compared with control mice (n = 8–11 mice/group). (C) The mRNA levels of CCL2, IL-1β and CXCL10 were increased in cultured astrocytes from Tsc1GFAPCKO mice compared with astrocytes from control mice (n = 5–9 mice/group). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, versus control mice by Student’s t test. (D) Seven days of rapamycin treatment (3 mg/kg/d i.p.) significantly inhibited the mRNA levels of CCL2, IL-1β and CXCL10 in the brains of Tsc1GFAPCKO mice compared with vehicle-treated Tsc1GFAPCKO mice (n = 4–12 mice/group). (E) Rapamycin treatment (2 ng/ml for 16 hours) significantly inhibited the mRNA levels of CCL2 and CXCL10, but not IL-1β, in cultured astrocytes from Tsc1GFAPCKO mice (n = 5–12 mice/group). * p<0.05 versus control mice, # p < 0.05 versus vehicle-treated Tsc1GFAPCKO mice by one-way ANOVA. Cont = control mice, KO = Tsc1GFAPCKO, Veh = vehicle, Rap = Rapamycin.