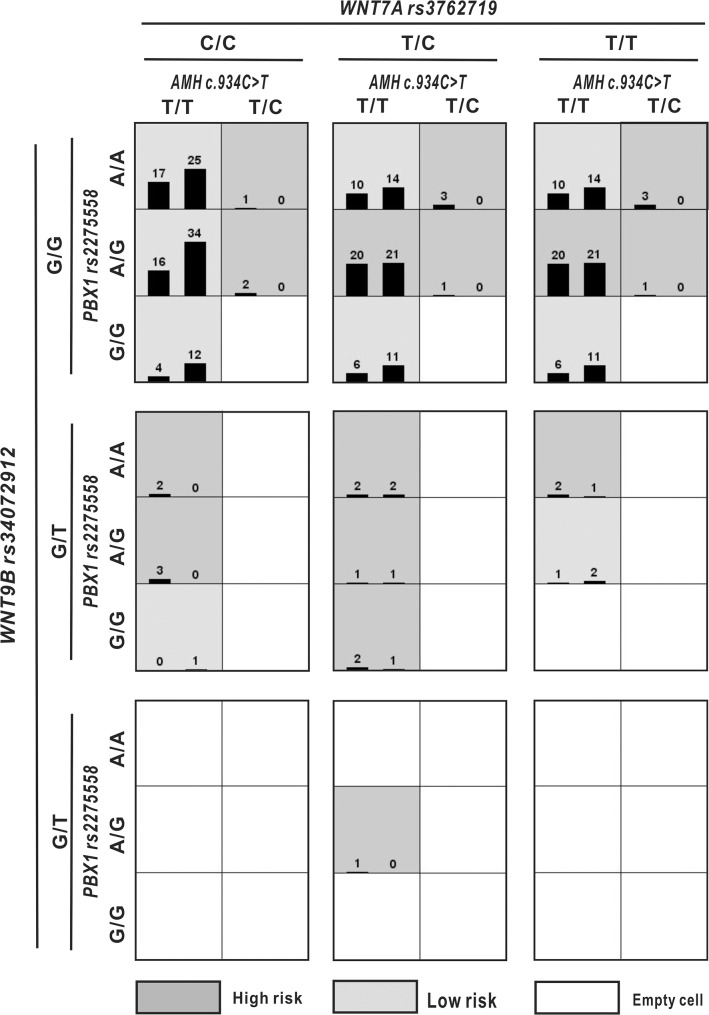
Fig 2. The optimal models as determined by MDR analysis for AMH c.934C>T, PBX1 rs2275558, WNT7A rs3762719 and WNT9B rs34072914.
Summary of four-locus genotype combinations associated with a high risk and low risk of MRKH syndrome, with the corresponding distribution of cases (left bars in boxes) and of controls (right bars in boxes), for each multi-locus-genotype combination. The four-locus model (AMH c.934C>T, PBX1 rs2275558, WNT7A rs3762719 and WNT9B rs34072914) was found to result in an increased the risk of MRKH syndrome (OR = 2.268, 95%CI = 1.494–3.443).